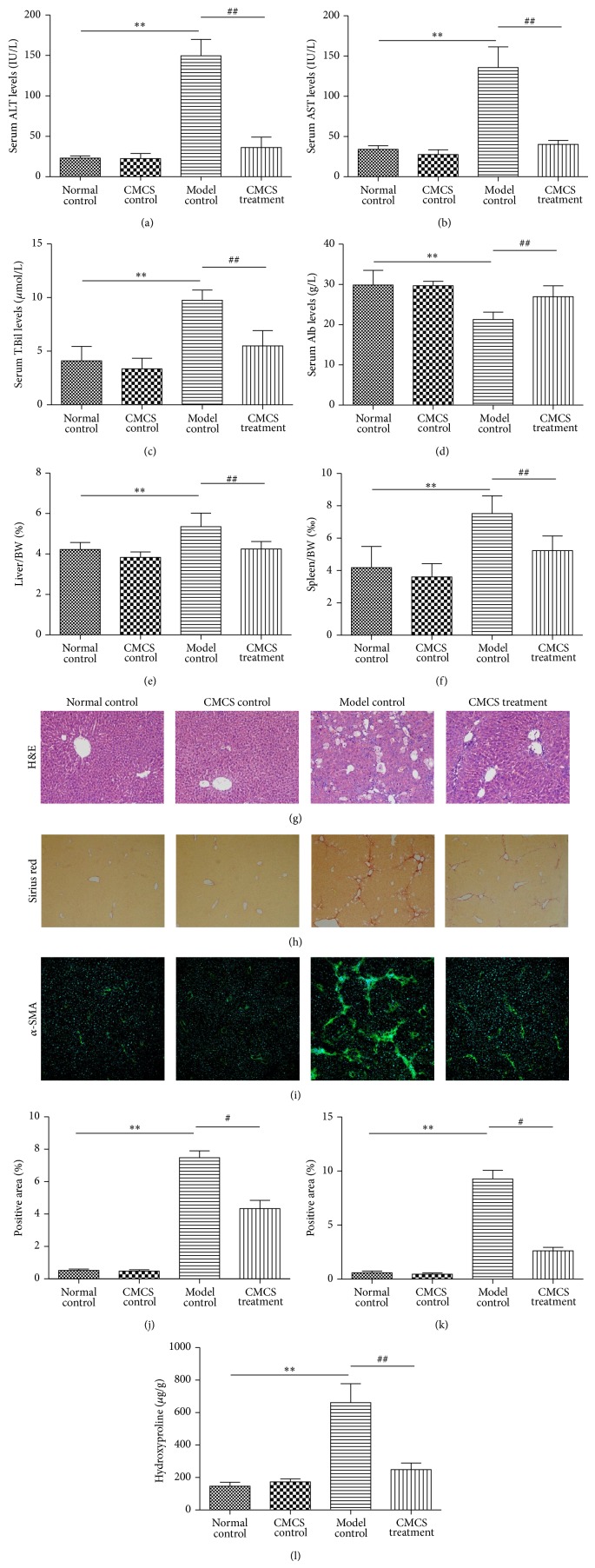
Figure 1.
Antifibrotic effects of CMCS on CCl4-induced liver fibrosis in mice. Mice of ten-week old were treated as described in the legend. Serum ALT (a), AST (b), Alb (c), and T.Bil (d) were assessed by liver function tests kits, respectively. Levels of serum liver functions were decreased, and liver/BW (e) and spleen/BW (f) were alleviated by CMCS treatment in CCl4-induced liver fibrosis mice. Histologic evaluation of liver tissues were stained with H&E ((g), ×200). Collagen deposition was revealed with Sirius Red staining ((h), ×100) and was shown as the proportion of Sirius red-positive area (j). Expressions of α-SMA in liver tissues were analyzed by immunofluorescent staining. Representative bright-field and fluorescent micrographs were shown ((i), ×100). Semiquantification of α-SMA expression was evaluated and shown as percentage of α-SMA-positive areas (k). Hydroxyproline content was quantified from 100 mg liver samples and was measured by Jamall's method (l). * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.001, versus Normal control; # P < 0.05, ## P < 0.001, versus Model control.