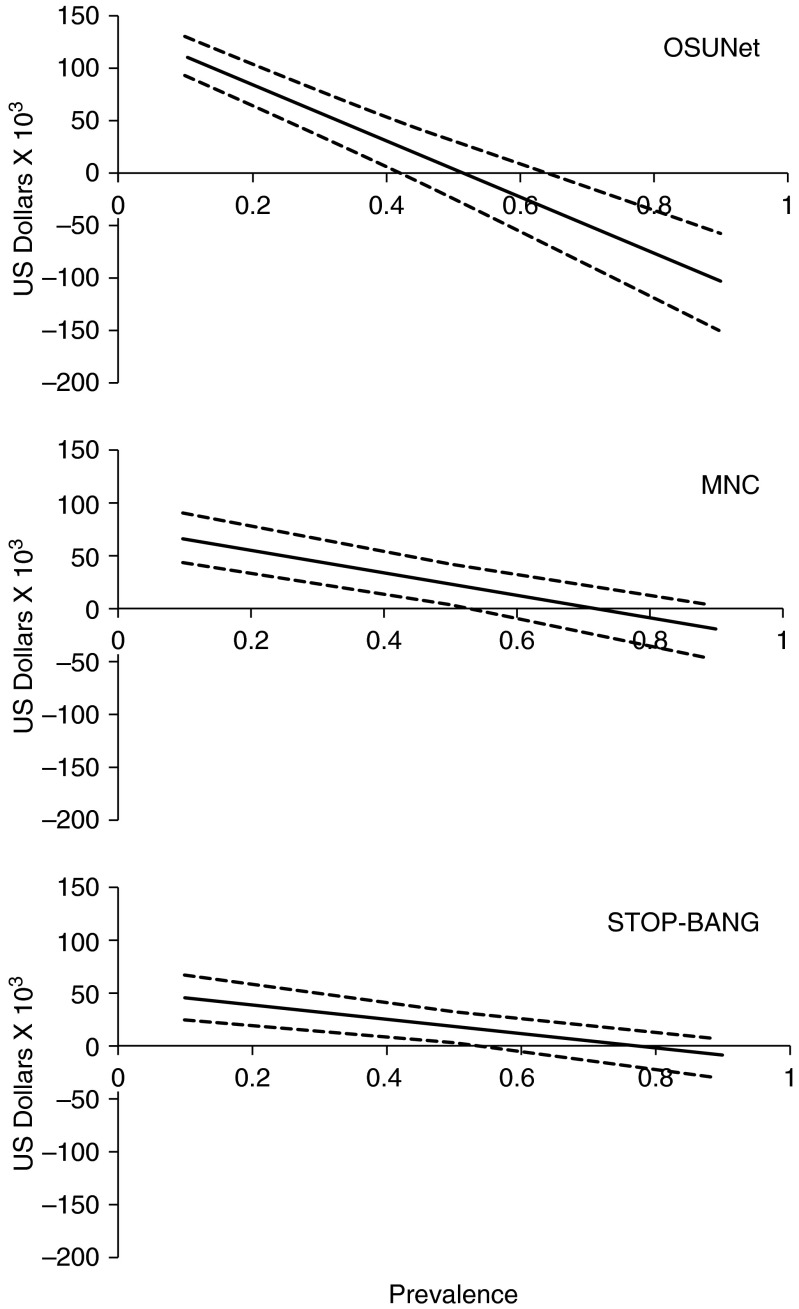
Figure 3.
Cost savings from the use of prediction tools using an apnea–hypopnea index (AHI) of at least 15/hour to define the presence of obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). (A) Savings per 1,000 patients using the OSUNet to select patients to undergo a home sleep test (HST) as the initial diagnostic procedure according to prevalence of OSA. (B) Savings per 1,000 patients using the modified neck circumference (MNC) to select patients to undergo HST as the initial diagnostic procedure according to prevalence of OSA. (C) Savings per 1,000 patients using the STOP-BANG to select patients to undergo HST as the initial diagnostic procedure according to prevalence of OSA. The dashed lines represent the corresponding 95% confidence intervals. STOP-BANG, Snoring, Tiredness, being Observed to stop breathing during sleep, high blood Pressure, Body mass index greater than 35 kg/m2, Age greater than 50 years, Neck circumference greater than 40 cm, and male Gender.