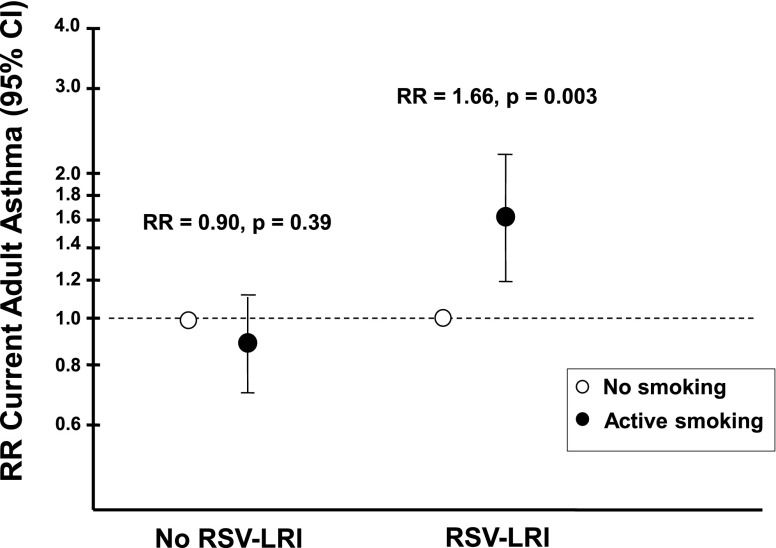
Figure 1.
Adjusted relative risk of current adult asthma by smoking status among subjects with and without early-life respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) lower respiratory illness (LRI). Among subjects with early RSV-LRI, active smoking was associated with an increased risk of current asthma (relative risk [RR], 1.66; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.19–2.31; P = 0.003). The effect of smoking on asthma was not observed among those without an early RSV-LRI (RR, 0.90; 95% CI, 0.70–1.15; P = 0.39). Data were analyzed by generalized estimating equation adjusted for age, sex, parental asthma, and maternal smoking at enrollment.