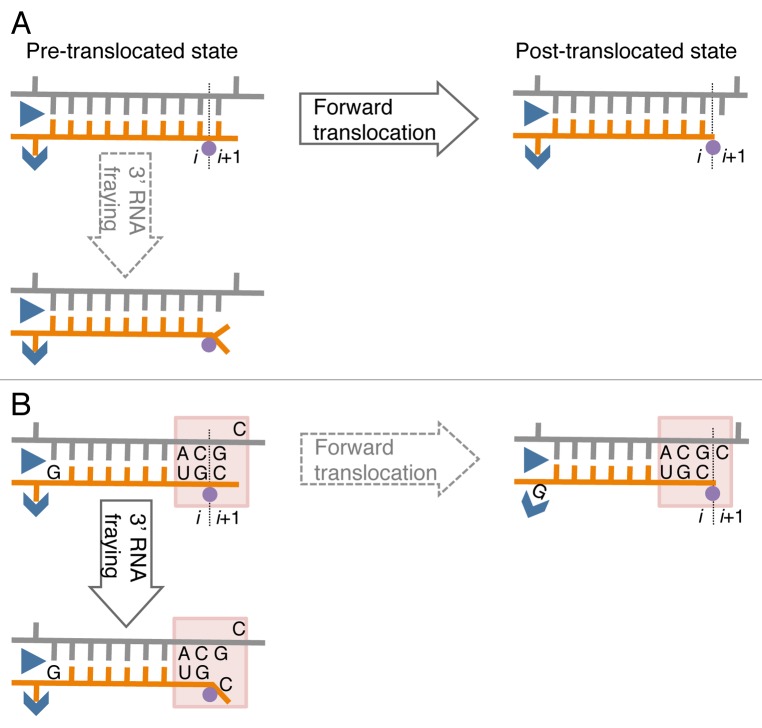
Figure 1. A model of sequence-specific pausing. (A) Pause-free elongation. RNA (orange), template DNA strand (gray), catalytic Mg2+ (magenta circle), and two RNAP domains (blue) involving 5′ RNA separation from the hybrid, i.e., Switch 3 (arrow head) and lid (triangle) domains are shown. The 3′ RNA-binding site (i) and the NTP binding site (i+1) are also indicated. (B) Elongation at the pausing site. The two sequence elements involved in transcription pausing are shown: (1) 3′ ACGC 5′ sequence in the transcribed DNA strand (grey) corresponding to the junction between the RNA-DNA hybrid and the downstream dsDNA in the elongation complex (indicated by shaded box); this sequence increases mobility/flexibility of the RNA/DNA backbones, which promotes fraying of the 3’ RNA end. (2) G residue in the RNA at the upstream end of the hybrid contributes to immobilization of the hybrid in the catalytic cleft of RNAP by interacting with the Switch 3 domain in the post-translocated state, or by interacting with the lid domain in the pre-translocated state.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.