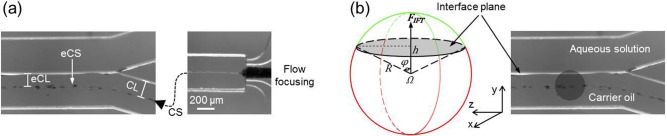
Attenuation of the CL into eCL and the unbalanced hydrophobic force (
FIFT) as a result of the intrinsic interfacial tension between oil and hydrogel microparticle. (a) On the right, a typical image showing visualization of the CS of carrier oil emulsion by injecting dye Amaranth in the middle channel of flow focusing at a low flow rate (0.06 ml/h) and on the left, a typical image showing visualization of the CL and eCL by tracking the CS and eCS of carrier oil emulsion using Amaranth dye. The flow rate of carrier oil emulsion and aqueous extracting solution is all 5.5 ml/h. (b) On the right, the same image on the left of panel (a) overlaid with an imaginary hydrogel microparticle and on the left, a schematic illustration of the unbalanced hydrophobic force
FIFT imposed on the hydrogel microparticle as a result of the intrinsic interfacial tension between oil and hydrogel microparticle.
R is the radius of hydrogel microparticle,
h is the distance from the interface plane to microparticle center,
φ is the half of the 2D apex angle of the extracted surface (green), and
Ω is the 3D solid angle of the non-extracted surface (red). (Multimedia view) [URL:
http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.4898040.1]
Download video file (79.8KB, mov) DOI: 10.1063/1.4898040.1