Figure 2.
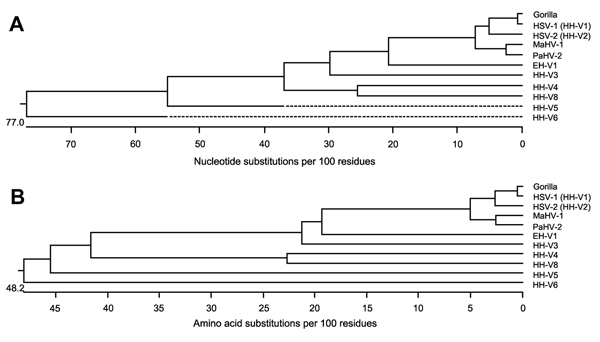
Phylogenetic analysis of the nucleotide sequence (A) and predicted amino acid sequence (B) from the swab sample amplicon from the gorilla with the corresponding regions of HSV-1 (HHV-1; GenBank accession no. AFI98948); HSV-2 (HHV-2; AGI44412); MaHV-1 (AAT67222); PaHV-2 (YP_443877); HHV-3 (varicella zoster virus; ABF21820); HHV-4 (Epstein-Barr virus; YP_401712); HHV-5 (human cytomegalovirus; AAP37469); HHV-6 (BAF93477); HHV-8 (Kaposi sarcoma virus; ACY00400), and EHV-1 ADI96155). Sequences were aligned by the Clustal W method (http://www.clustal.org) by using the MegAlign (DNAStar, Madison, WI, USA) sequence alignment program (multiple alignment parameters: gap penalty = 15.00; gap length penalty = 6.66; delay divergent seqs (%) = 30; DNA transition weight = 0.50. Pairwise alignment parameters: slow-accurate; gap penalty = 15.00; gap length = 6.66). EHV, equid herpesvirus; HSV, herpes simplex virus; HHV, human herpesvirus; MaHV, Macacine herpesvirus; PaHV, Papiine herpesvirus.
