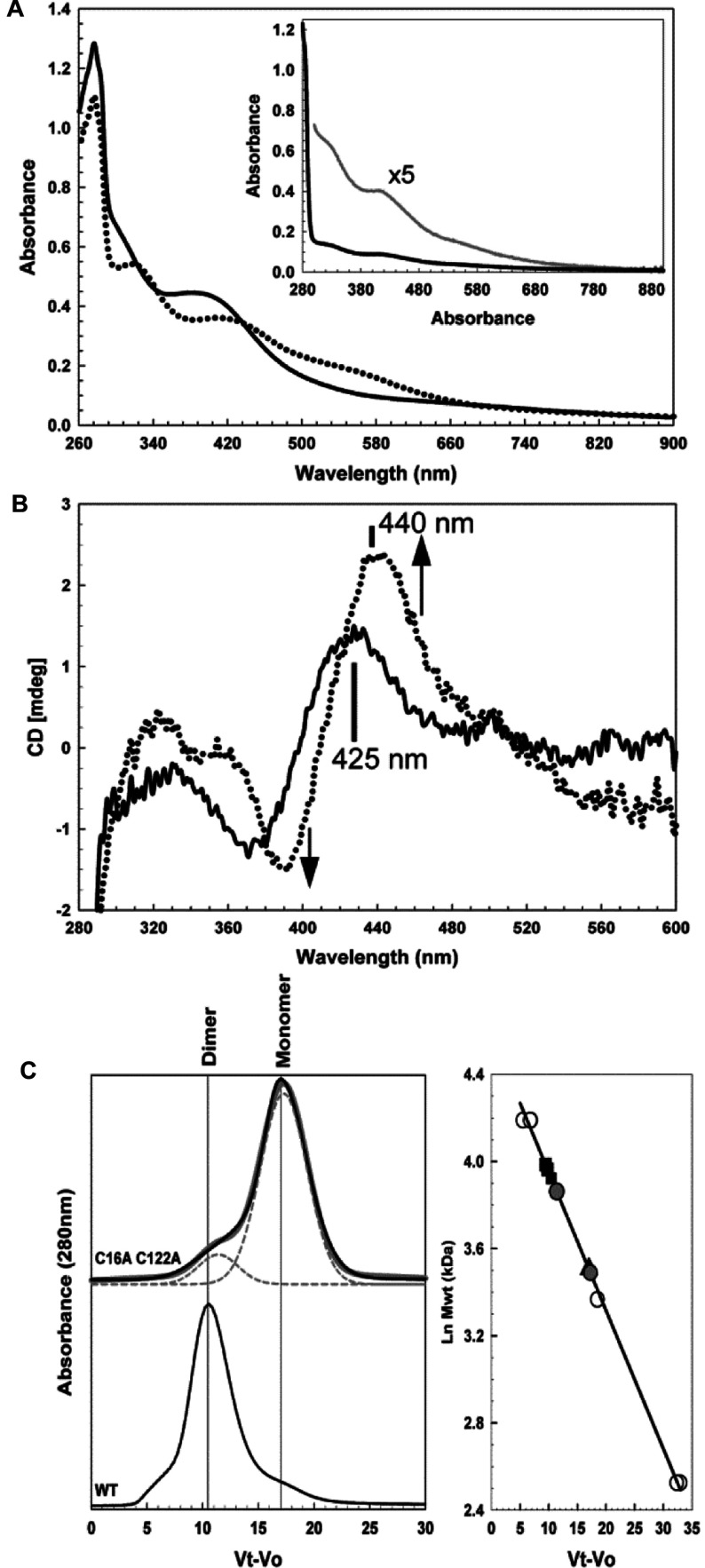
Figure 2. Optical properties of C16A/C122A FNR.
(A) Absorbance spectra and (B) CD spectra of reconstituted C16A/C122A FNR (~27 μM [4Fe-4S], 40% replete). In the presence (broken line) and absence (continuous line) of a 2-fold excess of O2. Inset, absorption spectrum of C16A/C122A FNR isolated under anaerobic conditions (black line), revealing the presence of a small amount (~4% replete) cluster (grey line). (C) The left-hand panel shows gel-filtration chromatography of C16A/C122A FNR (415 μM [4Fe-4S]). In grey is a fit of the chromatogram to multiple Gaussian peaks, revealing peaks corresponding to masses of 48 kDa and 33 kDa, accounting for ~20% and 80% of the total peak area respectively. The chromatogram of predominantly dimeric wild-type FNR (~70 μM [4Fe-4S], 94% replete) is shown below for comparison. The right-hand panel shows a calibration curve for the Sephacryl S100HR column. Open circles correspond to standard proteins (BSA, carbonic anhydrase and cytochrome c), black squares correspond to [4Fe-4S] wild-type FNR (54 kDa), black triangles correspond to [2Fe-2S] wild-type FNR (33 kDa) and grey circles correspond to C16A/C122A FNR peaks. The buffer was 25 mM Hepes, 2.5 mM CaCl2, 100 mM NaCl and 100 mM NaNO3 (pH 7.5).