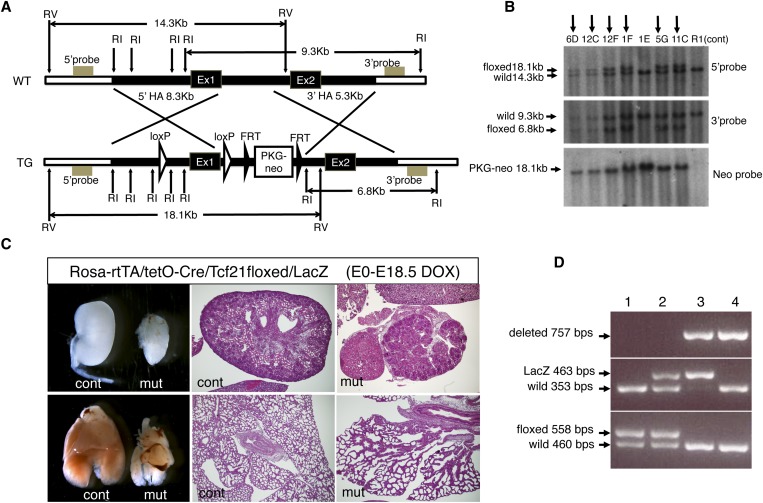
Figure 1.
Generation of conditional allele for Tcf21. (A) Targeting construct for floxed Tcf21 allele. LoxP sites were inserted around exon1 (Ex1). FRT, FRT sequence; HA, homology arm; RI, EcoRI site; RV, EcoRV site; TG, targeted; WT, wild type. (B) Targeted clones were identified by Southern blot analysis using probes outside the 5′ and 3′ homology arms. Arrows indicate positively targeted clones. Clones 12F and 5G were used for ES cell aggregation; only the 5G clone resulted in germline transmission. (C) Validation of the floxed allele using the Rosa-rtTA/tetO-Cre system. Doxycycline induction to excise the floxed alleles in embryos from E0 (conception) resulted in a phenotype in newborn pups identical to that observed in conventional Tcf21 knockout pups. Note the severely hypoplastic kidneys (upper panels) and lungs (lower panels) in floxed mutants. Histology, hematoxylin and eosin; original magnification, ×40. (D) PCR genotyping shows floxed Tcf21 allele (558 bp), Tcf21-LacZ allele (463 bp; conventional knockout), and floxed allele after Cre-mediated deletion (757 bp). Lane 3 shows the genotype from a mouse carrying one deleted floxed allele and a null LacZ allele. cont, control littermate; DOX, doxycycline; mut, mutant, Rosa-rtTA/tetO-Cre/Tcf21floxed/LacZ.