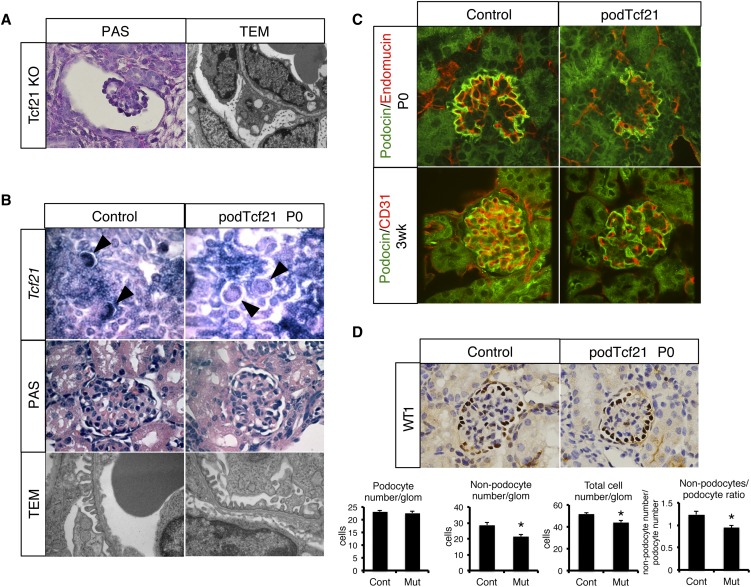
Figure 2.
Delay of glomerular maturation in podTcf21 mice. (A) Periodic acid-Schiff (PAS)–staining (×1000) of a glomerulus and a TEM (×12,400) of the glomerular barrier in the kidney from conventional Tcf21 knockout at E18.5. (B) Upper panel: in situ hybridization for Tcf21 (×200) confirms loss of Tcf21 message in capillary loop stage podocytes in podTcf21 mice (arrowheads). Middle panel: periodic acid-Schiff–staining of glomeruli (×1000). Lower panel: TEM that shows relatively normal glomerular filtration barrier of podTcf21 at postnatal day 0 (P0) (×12,400). (C) Immunostainings for endothelial (CD31 or endomucin) markers and podocin demonstrate simplified structure of the glomerulus at P0 (upper) and 3 weeks (lower) in podTcf21 mice compared with control (×400). (D) Reduced nonpodocyte cell number in podTcf21 glomeruli. Upper panel: immunostainings for a podocyte marker, Wt1 (×1000). Lower panels: numbers of podocytes, non-podocytes, total cell number in each glomerulus, and non-podocyte/podocyte ratio. Total cell number and non-podocyte cell number in mutant glomeruli were reduced by 15% (51.8 cells in control versus 44.1 cells in podTcf21; P<0.05) and 25% (28.6 cells in control versus 21.4 cells in podTcf21; P<0.05), respectively. *P<0.05.