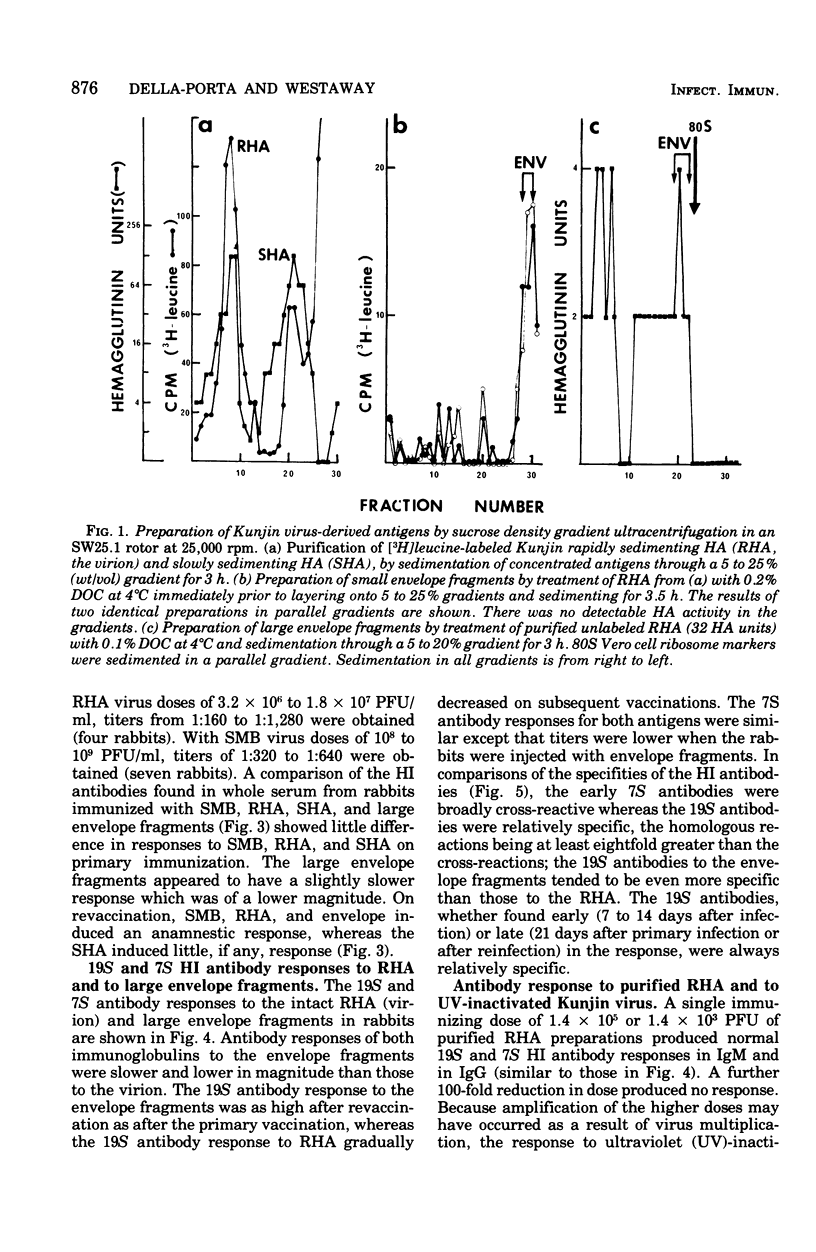
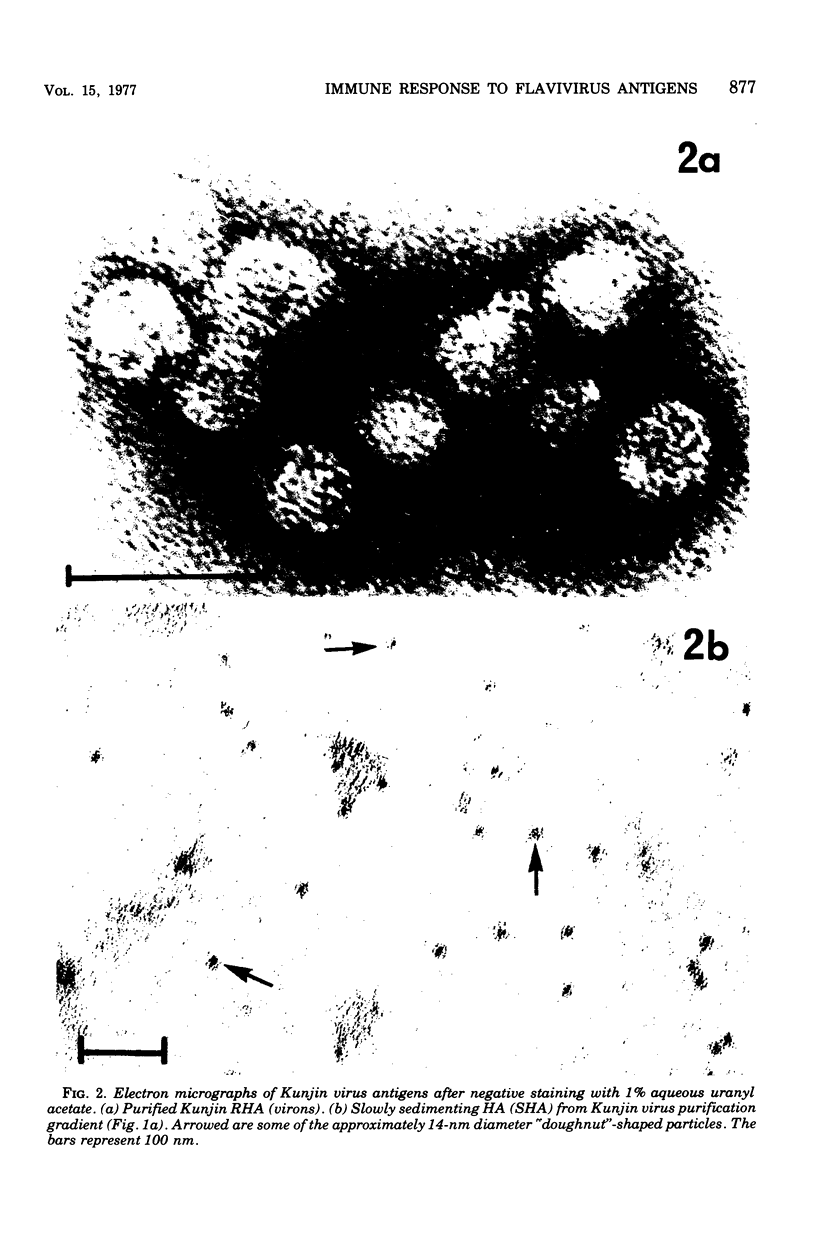
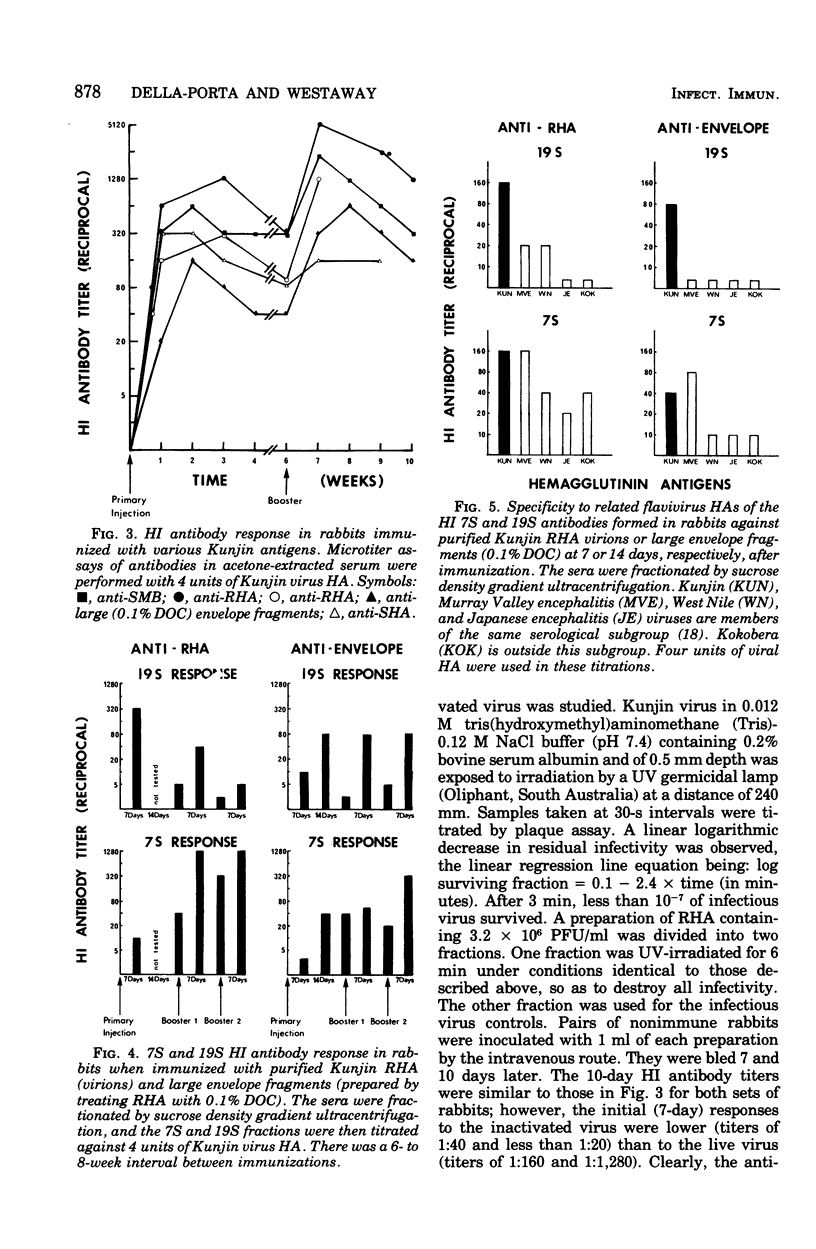
Abstract
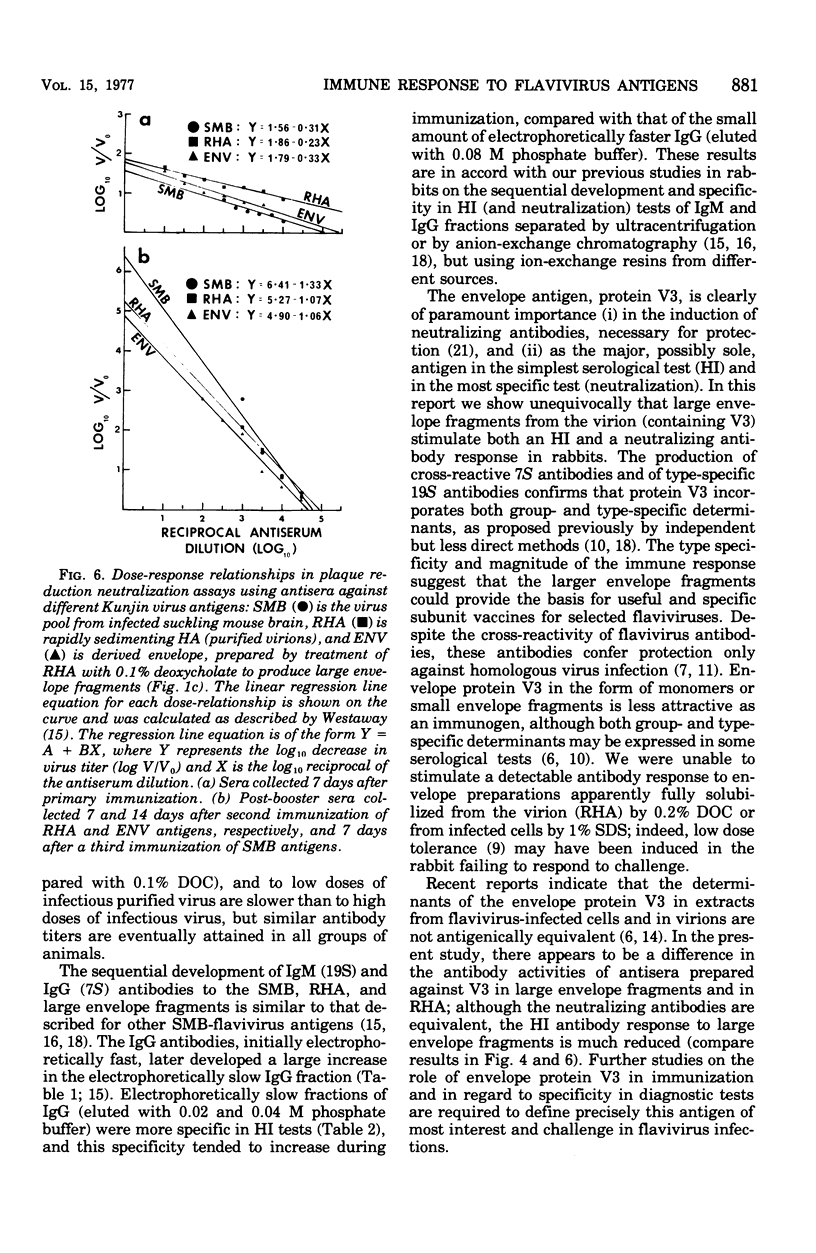
The nature of the antibodies formed in rabbits in response to the following Kunjin virus antigens was examined: infectious suckling mouse brain (SMB), purified virion or rapidly sedimenting hemagglutinin (RHA), slowly sedimenting hemagglutinin (SHA), and envelope fragments prepared from RHA disrupted by 0.1 or 0.2% sodium deoxycholate (DOC). The hemagglutination-inhibiting (HI) and neutralizing antibody responses to SMB, RHA, and large envelope fragments (0.1% DOC) were remarkably uniform, antibodies appearing at the same time, attaining similar HI titers (lowest to envelope), and being of similar avidity early and late in the respone. The 19S (immunoglobulin M) antibodies to all antigens were always relatively type-specific, whereas the 7S (immunoglobulin G) antibodies were always broadly cross-reactive in HI tests. These results confirm that the envelope antigen is the principal antigen involved in the stimulation of protective neutralizing antibodies and contains both type- and group-specific antigenic determinants. The results also establish that there is no significant advantage in using purified RHA or SHA either for immunization or as hemagglutinin antigens in attempts to obtain greater specificity in the HI test. No differences were detected in the antibody responses to infective Kunjin virus, within the range 1,400 to 10(9) plaque-forming units (PFU). Below 1,400 PFU, there was no detectable response. Inactivated virus (10(6) PFU) also stimulated the normal antibody response. In contrast, small envelope fragments (derived with 0.2% DOC) and a detergent-solubilized extract of infected cells were unable to stimulate a detectable antibody response and the small envelope fragments may have induced low dose tolerance in one of two rabbits.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ADA G. L., ABBOT A., ANDERSON S. G., COLLINS F. D. Particle counts and some chemical properties of Murray Valley encephalitis virus. J Gen Microbiol. 1962 Sep;29:165–170. doi: 10.1099/00221287-29-1-165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLARKE D. H., CASALS J. Techniques for hemagglutination and hemagglutination-inhibition with arthropod-borne viruses. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1958 Sep;7(5):561–573. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1958.7.561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cardiff R. D., Brandt W. E., McCloud T. G., Shapiro D., Russell P. K. Immunological and biophysical separation of dengue-2 antigens. J Virol. 1971 Jan;7(1):15–23. doi: 10.1128/jvi.7.1.15-23.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chernesky M. A., Whittaker-Haines P. J. Dose-dependent viremia and the differential immunoglobulin response of hamsters to Powassan virus. Can J Microbiol. 1972 May;18(5):655–661. doi: 10.1139/m72-103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Della-Porta A. J., Westaway E. G. Rapid preparation of hemagglutinins of togaviruses from infected cell culture fluids. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Jan;23(1):158–160. doi: 10.1128/am.23.1.158-160.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckels K. H., Hetrick F. M., Russell P. K. Virion and soluble antigens of japanese encephalitis virus. Infect Immun. 1975 May;11(5):1053–1060. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.5.1053-1060.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman R., Pariyanonda A. Human immunoglobulin M antibody in the sero-diagnosis of Japanese encephalitis virus infections. Am J Epidemiol. 1973 Jul;98(1):29–38. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a121529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason R. A., Tauraso N. M., Ginn R. K., O'Brien T. C., Trimmer R. W. Yellow fever vaccine. V. Antibody response in maonkeys inoculated with graded doses of the 17D vaccine. Appl Microbiol. 1972 May;23(5):908–913. doi: 10.1128/am.23.5.908-913.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qureshi A. A., Trent D. W. Group B arbovirus structural and nonstructural antigens. 3. Serological specificity of solubilized intracellular viral proteins. Infect Immun. 1973 Dec;8(6):993–999. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.6.993-999.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott R. M., McCown J. M., Russell P. K. Human immunoglobulin specificity after group B arbovirus infections. Infect Immun. 1972 Sep;6(3):277–281. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.3.277-281.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro D., Brandt W. E., Cardiff R. D., Russell P. K. The proteins of Japanese encephalitis virus. Virology. 1971 Apr;44(1):108–124. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90158-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith T. J., Brandt W. E., Swanson J. L., McCown J. M., Buescher E. L. Physical and biological properties of dengue-2 virus and associated antigens. J Virol. 1970 Apr;5(4):524–532. doi: 10.1128/jvi.5.4.524-532.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stohlman S. A., Eylar O. R., Wisseman C. L., Jr Isolation of the dengue virus envelope glycoprotein from membranes of infected cells by concanavalin A affinity chromatography. J Virol. 1976 Apr;18(1):132–140. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.1.132-140.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
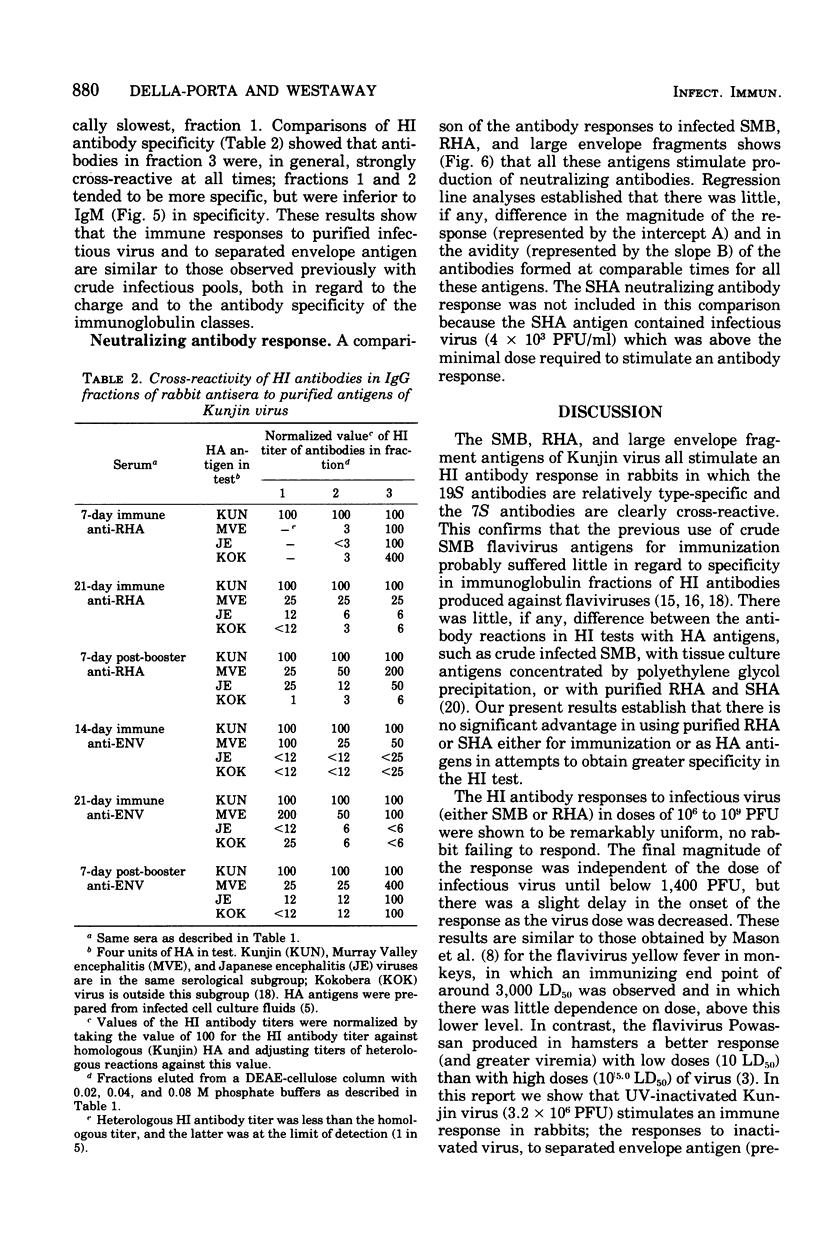
- Westaway E. G. Antibody responses in rabbits to the group B arbovirus Kumjin: serologic activity of the fractionated immunoglobulins in homologous and heterologous reactions. J Immunol. 1968 Mar;100(3):569–580. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westaway E. G., Della-Porta A. J., Reedman B. M. Specificity of IgM and IgG antibodies after challenge with antigenically related togaviruses. J Immunol. 1974 Feb;112(2):656–663. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westaway E. G. Greater specificity of 19S than 7S antibodies on haemagglutination-inhibition tests with closely related group B arboviruses. Nature. 1968 Jul 6;219(5149):78–79. doi: 10.1038/219078a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westaway E. G. Proteins specified by group B togaviruses in mammalian cells during productive infections. Virology. 1973 Feb;51(2):454–465. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90444-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westaway E. G., Shew M., Della-Porta A. J. Reactions of purified hemagglutinating antigens of flaviviruses with 19S and 7S antibodies. Infect Immun. 1975 Apr;11(4):630–634. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.4.630-634.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zisman B., Wheelock E. F., Allison A. C. Role of macrophages and antibody in resistance of mice against yellow fever virus. J Immunol. 1971 Jul;107(1):236–243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]