Table 1. Model parameters.
| Parameter | Realistic Value | Description | Reference |
| n | 1–8 | Number of epitopes recognized during first 100 days | [11], [13], [30], [31] |
| m | 2–10 | Number of sites per epitope important for recognition | [11], [13], [30], [31] |
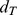
|
1 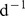
|
Rate at which activated target cells transition out of the highly infectable phase | [46], [68] |
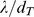
|
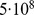 cells cells |
Activated target cell level | [47], [69], [70] |
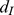
|
1 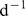
|
Virus-induced infected cell death rate | [55] |
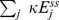
|
4 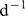
|
CTL-induced infected cell death rate | [47], [69], [70] |
| β |
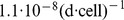
|
Basic efficiency of target cell infection | [47], [69], [70] |
| s |
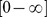
|
Intrinsic mutation cost | [10], [21], [22], [27]–[29] |
| α |
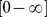
|
Reduction of CTL recognition | [27]–[29] |
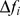
|
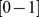
|
Fractional reduction in intrinsic replication rate | |
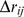
|
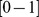
|
Fractional reduction of CTL recognition | |

|
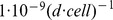
|
CTL killing efficiency. Gives 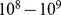 CTLs in chronic infection CTLs in chronic infection |
[45] |
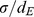
|
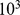 cells cells |
Initial population of CTLs | [69] |
| c | 1 
|
Maximum growth rate of effector cells | [69] |
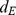
|
0.1 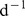
|
Death rate of effector cells | [47], [69], [70] |
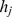
|
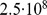 cells cells |
Number of recognized infected cells for half maximal proliferation of CTL (inverse avidity). Gives an infected cell level of 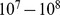 in chronic infection in chronic infection |
[44] |
Model parameters for the model of escape from multiple CTL shown in Figure 1.
