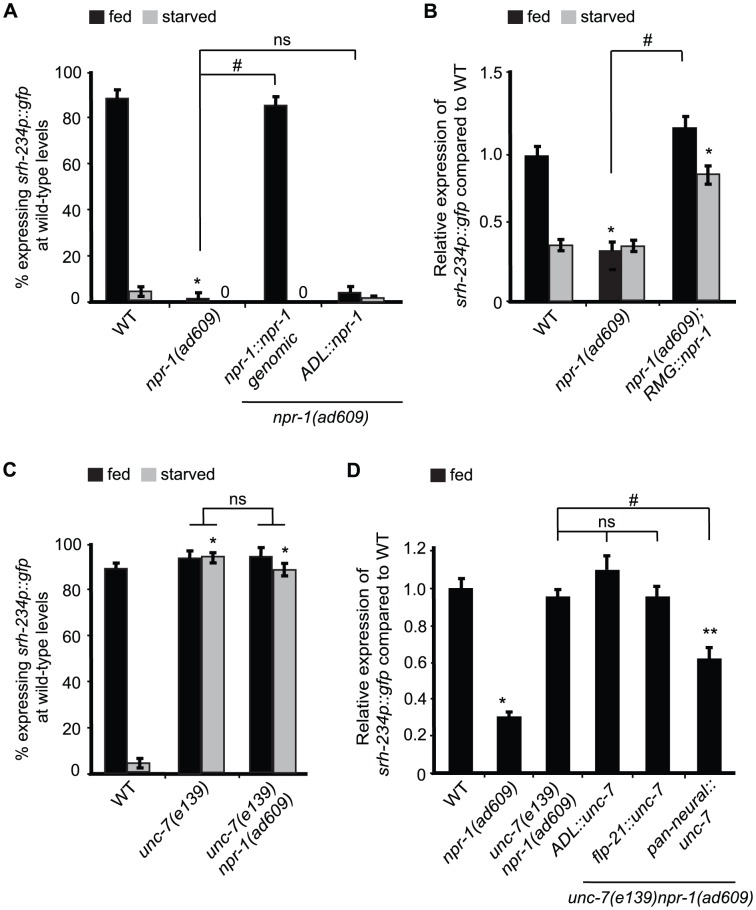
Figure 4. Reducing npr-1 activity in RMG promotes srh-234 expression levels.
A) Percentage of npr-1 mutant animals expressing srh-234p::gfp at wild-type levels. For strains carrying the npr-1::npr-1 genomic and ADL::npr-1 extrachromosomal arrays (see Material and Methods), data shown is the average of at least two independent transgenic lines. Animals (n>150) were examined at 150× magnification for each genotype. B) Relative expression of srh-234p::gfp in npr-1 mutants compared to wild-type. For strains carrying RMG::npr-1 extrachromosomal arrays (see Material and Methods), data shown is for at least two independent transgenic lines. Animals (n = 20–23) were examined at 400× magnification for each genotype. C) Percentage of animals of the indicated genotypes expressing srh-234p::gfp at wild-type levels. Animals (n>150) were examined at 150× magnification for each genotype. D) Relative expression of srh-234p::gfp in unc-7 npr-1 double mutants compared to wild-type. For strains carrying ADL::unc-7L cDNA, flp-21::unc-7L cDNA and pan-neural::unc-7L cDNA extrachromosomal arrays (see Material and Methods), data shown is for at least two independent transgenic lines. Animals (n = 15–22) were examined at 400× magnification for each genotype. In all experiments, * indicates values that is different from that of wild-type animals at P<0.001, and # indicates the values that are different between the genotypes compared by brackets at P<0.001 using either a χ2 test of independence or using a two-sample t-test. n.s. indicates the values between brackets that are not significantly different. Error bars denote the SEM or SEP.