Figure 7. Model for sensory and circuit-mediated regulation of srh-234 expression.
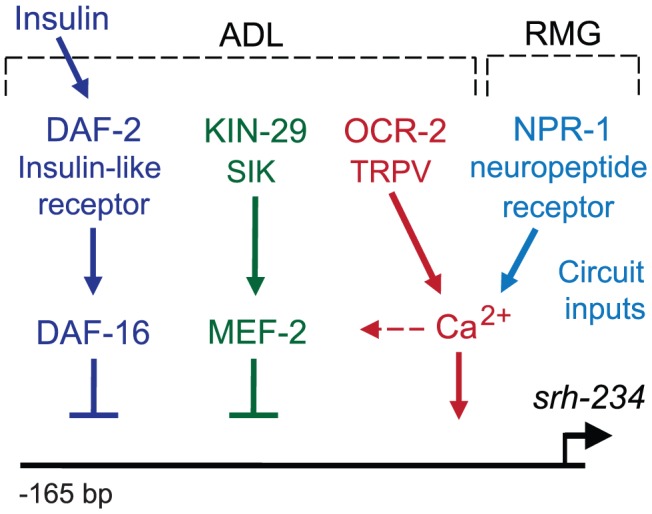
Expression levels of srh-234 are modulated by integration of sensory and internal feeding state signals via multiple pathways. During feeding, srh-234 expression is promoted by kin-29 salt-inducible kinase, daf-2 insulin-like receptor, and ocr-2 TRPV channel in ADL, and the npr-1 neuropeptide receptor in RMG interneurons. Negative transcriptional regulators of srh-234 expression, mef-2 and daf-16, act genetically downstream of kin-29 and daf-2, respectively, and likely act in parallel to ocr-2 and npr-1 pathways. The epistatic relationship between the different signaling pathways in ADL neurons remains to be fully defined. Unknown insulin-like peptides secreted by ADL or other neurons lead to activation of daf-2. Signaling mediated by kin-29, ocr-2, and npr-1, but less daf-2, converge on Ca2+ signaling, which likely affects activity-dependent transcription of chemoreceptor genes. After prolonged starvation, mef-2 and daf-16 may repress srh-234 expression, while yet unknown transcription factors may drive srh-234 expression during feeding.
