Figure 6. Co-operative interactions between leptin and CCK to regulate CART expression in vagal afferent neurons.
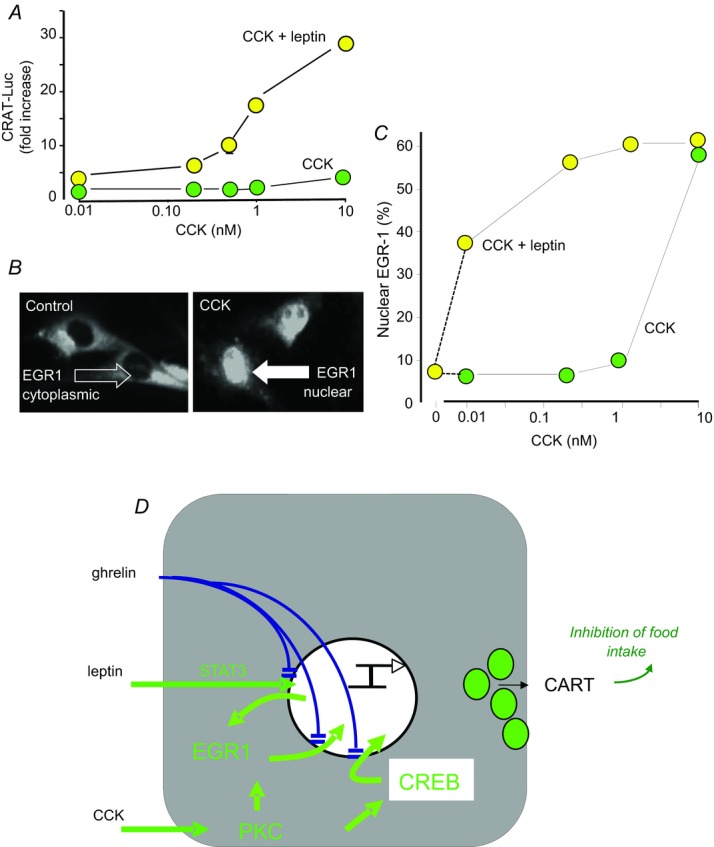
A, in cultured rat nodose ganglion neurons transfected with a CART promoter–luciferase reporter construct there is modest stimulation of CART expression by high concentrations of CCK, and there is strong potentiation by leptin. B, the immediate early gene EGR1, exhibits cytosolic localisation in unstimulated rat nodose ganglion neurons, but after CCK there is rapid nuclear translocation. C, stimulation of EGR1 nuclear translocation is strongly potentiated by leptin; leptin alone does not stimulate translocation. D, however, leptin stimulates EGR1 expression via STAT3. CCK does not stimulate EGR1 expression but acts via PKC and p42/44 MAP kinase to stimulate nuclear translocation which, together with activation of CREB, stimulates CART expression. Ghrelin inhibits nuclear translocation of STAT3, EGR1 and CREB thereby suppressing the effects of both leptin and CCK (de Lartigue et al. 2010).
