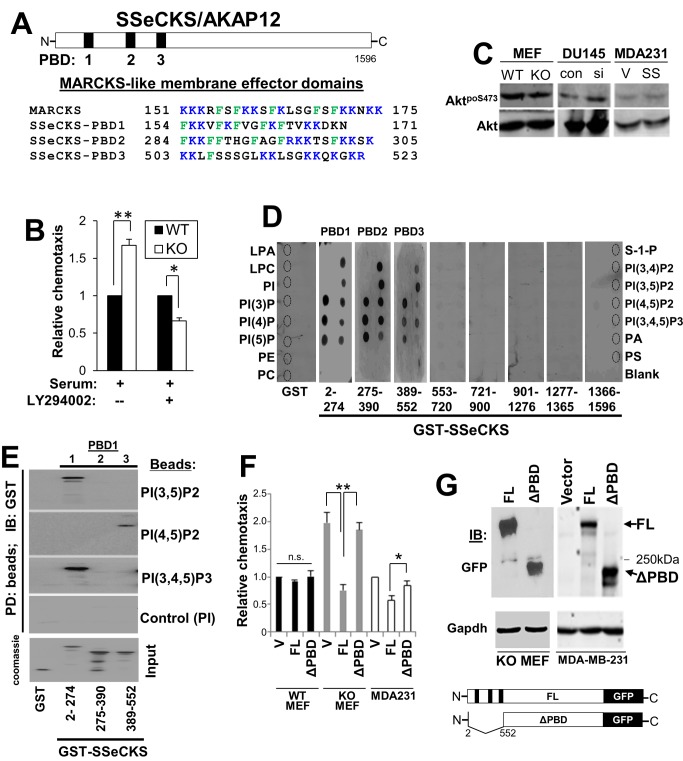
Figure 3. SSeCKS encodes three PBD that are required for inhibition of chemotaxis.
A, Location (top) and sequence (bottom; flanking residue numbers) of the SSeCKS PBD compared to the MARCKS membrane effector domain. B, WT or KO MEF were assessed for chemotaxis towards serum in the presence or absence of the PI3K inhibitor, LY29004. Error bars, S.E. of two independent experimental duplicates. *, p<0.02, **, p<0.01. C, IB analyses for AktpoS473 or total Akt in lysates of cells from Fig. 1B. D, Overlay assay of PIP-Strips with GST or GST-fusion proteins. Phospholipid spots (identified as broken-lined circles) are labeled on the left and right sides. Production of the GST and GST-SSeCKS fusion proteins is described in Guo et al. [29]. E, PIP-bead binding assay. PIP-beads binding to GST or GST-SSeCKS proteins (aliquots shown on a Coomassie-stained gel, bottom) were assessed by SDS-PAGE by IB for GST. F, FL SSeCKS, but not ΔPBD-SSeCKS, rescues chemotaxis inhibition (left panel) in KO MEF and MDA-MB-231, but not in WT MEF, compared to vector (V) alone. *, p<0.05, **, p<0.005. G, GFP-IB of full-length (FL) and ΔPBD SSeCKS-GFP proteins (arrows) expressed in KO MEF or MDA-MB-231 cells, compared to GADPH-IB as a loading control. Bottom- cartoon of FL- vs. ΔPBD SSeCKS-GFP constructs in which the 3-PBD (black bars) are lost in the a.a. 2–552 deletion. “250 kDa”, marker protein.