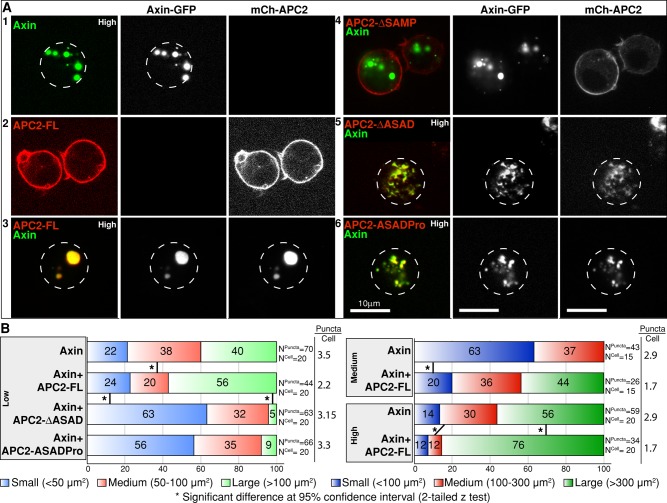
FIGURE 3:
Disruption of APC2 self-association leads to defects in destructosome assembly in live Drosophila S2 cells. In all cases, Axin is GFP tagged and APC2 is mCherry tagged. Dotted lines indicate cell boundaries. (A) When expressed alone in S2 cells, Axin-GFP oligomers can be visualized as cytoplasmic puncta (1), and mCh-APC2-FL (2) is primarily cortical. When coexpressed, mCh-APC2-FL colocalizes in cytoplasmic puncta with Axin-GFP (3). Removal of APC2's Axin interaction domains (APC2-∆SAMP) disrupts this colocalization (4). ASAD mutants (both ΔASAD and ASADPro) colocalize with Axin-GFP, but cells coexpressing these proteins exhibit defects in puncta assembly and morphology (5, 6). (B) Quantification of puncta size in S2 cells expressing Axin alone and coexpressing Axin and APC2 in cells sorted into three expression level categories (high, medium, and low) by FACS using Axin-GFP. Images were taken under the same imaging conditions, and puncta size was determined using Imaris. Puncta were then divided into three classes based on area (micrometers squared). Coexpression with APC2-FL is associated with fewer, larger puncta at all three expression levels (see puncta/cell ratios). Coexpression with the ASAD mutants showed increase in the number of small puncta only in the low category. Owing to the disrupted puncta morphology in ASAD mutants, we were only able to assess the puncta size in this category. Two-tailed z test demonstrates significant differences between different groups. Scale bar, 10 μm.