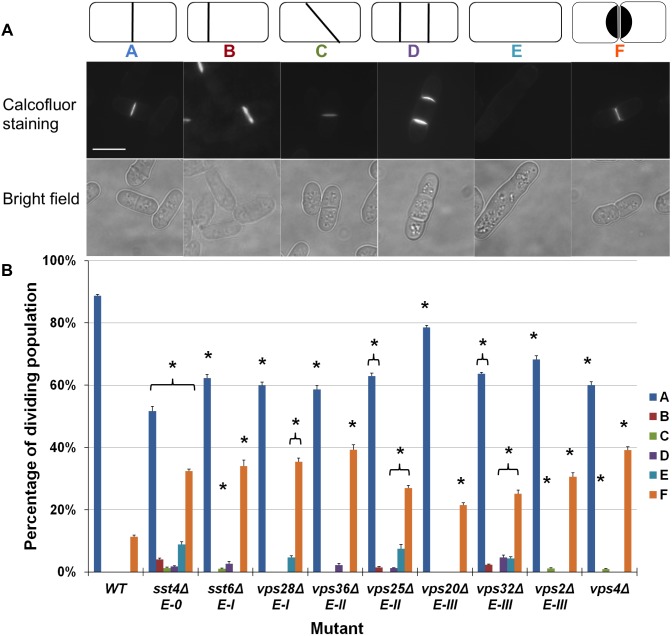
Figure 1. ESCRT proteins are required for septation in fission yeast.
(a) Defective septation in fission yeast strains containing chromosomal deletions of ESCRT genes. Wild-type and strains containing individual chromosomal deletions of ESCRT genes were grown at 25°C in complete liquid medium to mid-exponential phase and harvested. Cells were stained with Calcofluor white and visualised using fluorescence microscopy. Both fluorescence and bright field images are shown. Panels A-F show representative cells illustrating observed septation phenotypes. Schematic diagrams above panels represent each phenotype: (A) a normal septum, (B) a misaligned septum, (C) a non-perpendicular septum, (D) multiple septa, (E) no septal formation, and (F) failed separation of daughter cells following septation. Scale bars, 10 µm. Data from a typical experiment repeated three times is shown. (b) Quantitative analysis of the frequency of septation phenotypes A–F in strains containing ESCRT chromosomal deletions, in comparison to wild-type. In each case, 400 cells were counted in triplicate. An asterisk (*) indicates a p value<0.05, indicating a significant difference to wild-type; n = 3. Each of the ESCRT gene labels is accompanied by its respective ESCRT complex identification (E-0, E-I, E-II and E-III).