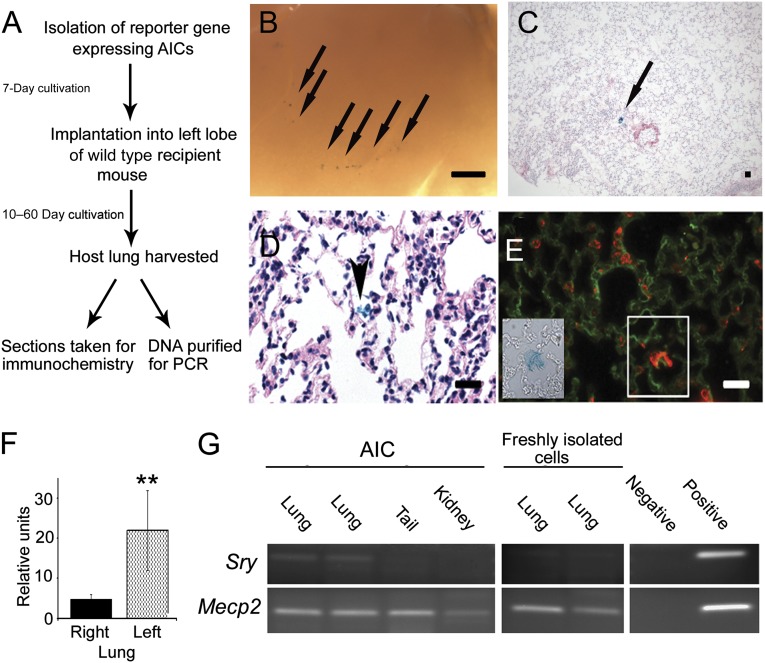
Figure 6.
Progenitor cell incorporation in the intact lung. (A): Flowchart depicting experiments of pulmonary isolation, transplantation (1 × 106 cells), and donor cell identification in recipient mouse lungs. (B): Macroscopic view of a day-10 post-transplantation lung grafted with β-galactosidase (β-gal)-expressing AICs. Scale bar = 1 mm. Arrows depict regions rich in indigo-stained cells. (C): Low power, hematoxylin eosin-stained section of a day 30 (post-transplantation) recipient lung demonstrating β-gal-positive cells in the alveolus (arrow). (D): High power, hematoxylin eosin-stained recipient lung section illustrating grafted β-gal-labeled cells (arrow) with connective tissue characteristics, bridging adjacent alveolar tissues. Scale bar = 100 μm. (E): High power image of a transplanted mouse alveolus collected at day 60 after transplantation demonstrating a region of prosurfactant protein C (red) and fibronectin-1 (green) expression (white box) that corresponds with β-gal-positive donor cell expression (inset). Scale bar = 50 μm. (F): Histogram comparing the average fluorescent intensities of selected ipsilateral and contralateral lung regions of mice (day 30 after transplantation) grafted with green fluorescent protein reporter cells. Differences in signal intensities are statistically significant (n = 4; p < .01, Wilcoxon test). Finally, male donor AICs or freshly isolated lung cells were transplanted into recipient female mice. After 30 days, distinct organs were harvested, and DNA was amplified. (G): Chromosome Y-linked Sry sequences were detected in the lungs but not in the tail or kidney of transplanted female mice at day 30. The X-linked Mecp2 gene, found in all cells, was used as a control. Implantation of freshly isolated cells (male, lung) did not show any retention in female recipients at the same time point. These differences are statistically significant (n = 4; p < .05). Negative and positive PCR controls represent no and male C57BL/6 DNA controls, respectively. Abbreviations: AIC, anchorage-independent cell; PCR, polymerase chain reaction.