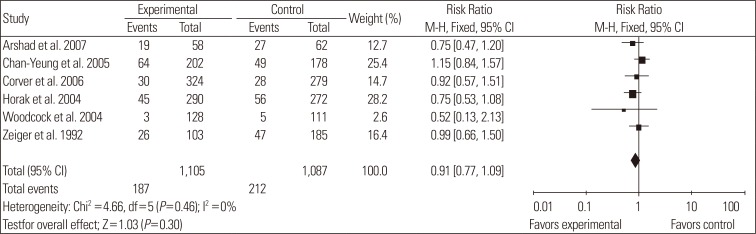
Fig. 3.
Forest plot showing the risk ratio for the incidence of rhinitis comparing allergen avoidance to the control in newborns with the potential to develop allergies. There was no significant difference between the experimental and control groups (P=0.30). Allergen avoidance did not improve the prevalence of rhinitis in high-risk infants.