FIGURE 1.
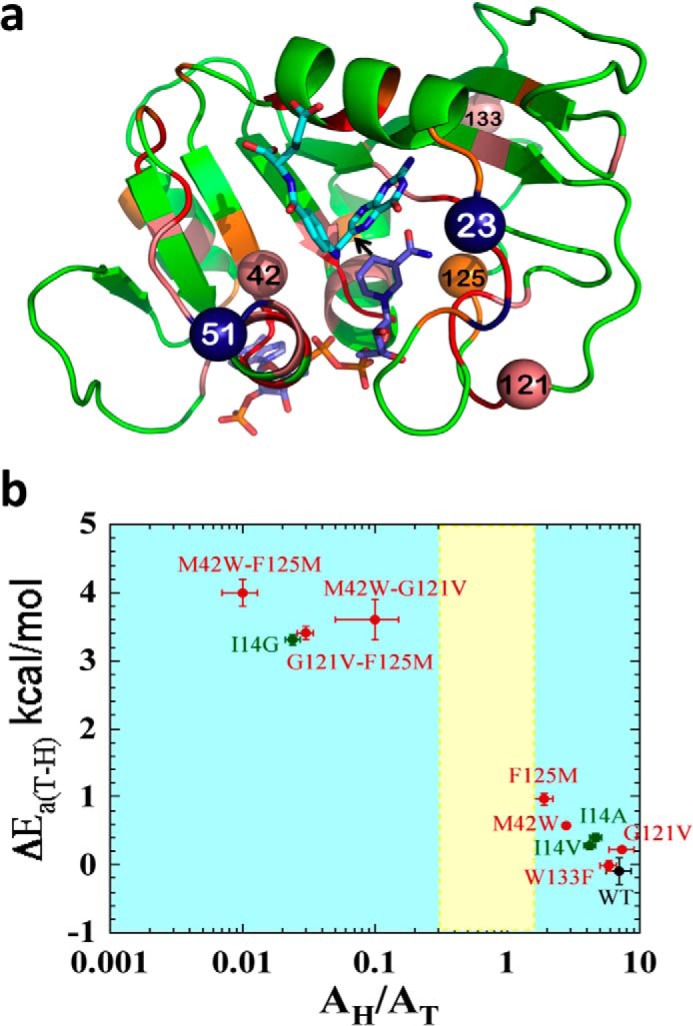
Structural, genetic, and functional features of DHFR. a, DHFR structure (Protein Data Bank (PDB) ID 1rx2) colored based on the genetic coupling analysis as Conserved (red), Strongly Coupled, (pink), and Weakly Coupled, (orange). The nicotinamide cofactor and folate are highlighted as blue and light blue sticks, respectively, and a black arrow is drawn at the location of the C–H→C transfer (between C4 of the nicotinamide to C6 of the pterin). Highlighted as spheres with the same color code are the α-carbons of the four coevolving residues that are discussed in the text above. Highlighted as dark blue spheres are Asn-23 and Gly-51, which are the sites of the evolution-induced insertions discussed below. b, correlation of temperature dependence parameters of T-KIEint for WT (black), distal (red), and active site Ile-14 (green) mutants of ecDHFR, where error bars represent S.D. The yellow block represents semi-classical range of Arrhenius pre-exponential factor (0.3–1.7) (46). Reproduced from Ref. 12. with permission from the American Chemical Society.
