FIGURE 6.
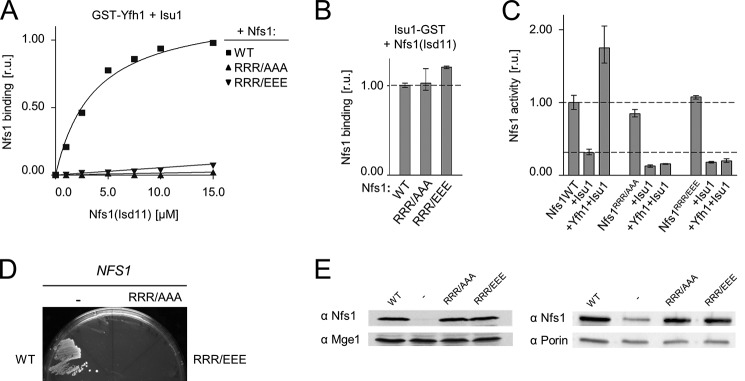
Replacement of residues Arg313, Arg316, and Arg318 of Nfs1 results in reduced binding of Yfh1 to the Isu1-Nfs1(Isd11) complex. A, 2.5 μm GST-Yfh1 was mixed with 15 μm Isu1 and the indicated concentrations of Nfs1(Isd11); wild-type (WT), Nfs1R313A/R316A/R318A (RRR/AAA), or Nfs1R313E/R316E/R318E (RRR/EEE). Glutathione resin was added to pull down GST-Yfh1 and associated proteins, which were separated by SDS-PAGE and stained. Densitometry values plotted as relative units (r.u.) with maximum binding of WT Nfs1 protein set at 1. B, 2.5 μm Isu1-GST was mixed with 15 μm Nfs1(Isd11) (WT) or the indicated replacement variants. Samples were treated and quantitated as in A. C, enzymatic activity of cysteine desulfurase Nfs1(Isd11) (WT) and the indicated replacement variants were measured in the absence and presence of other proteins, as indicated. Desulfurase activity of WT Nfs1(Isd11) alone was set to 1. B and C, bars represent average values for three independent measurements, with presented error bars indicating the range of the measurements. D, nfs1-Δ cells harboring an URA3-marked plasmid containing the WT copy of NFS1 and a second plasmid harboring either NFS1 (WT) or nfs1RRR/AAA or nfs1RRR/EEE or plasmid lacking an insert (−) were plated on glucose-minimal medium containing 5-fluoroorotic acid, which selects for cells having lost the plasmid containing the URA3 marker. The plate was incubated at 30 °C for 3 days. E, lysates of GAL-NFS1 cells transformed with plasmids having no insert (−) or harboring either a WT copy of NFS1 (WT), nfs1RRR/AAA, or nfs1RRR/EEE, as indicated, under the control of the native NFS1 promoter were prepared 24 h after transfer from galactose- to glucose-based medium and separated by SDS-PAGE. Immunoblots were probed with antibodies specific to Nfs1 and Mge1 (left) or porin (right), as a loading control. Left, whole cell lysates. Right, mitochondrial lysates.
