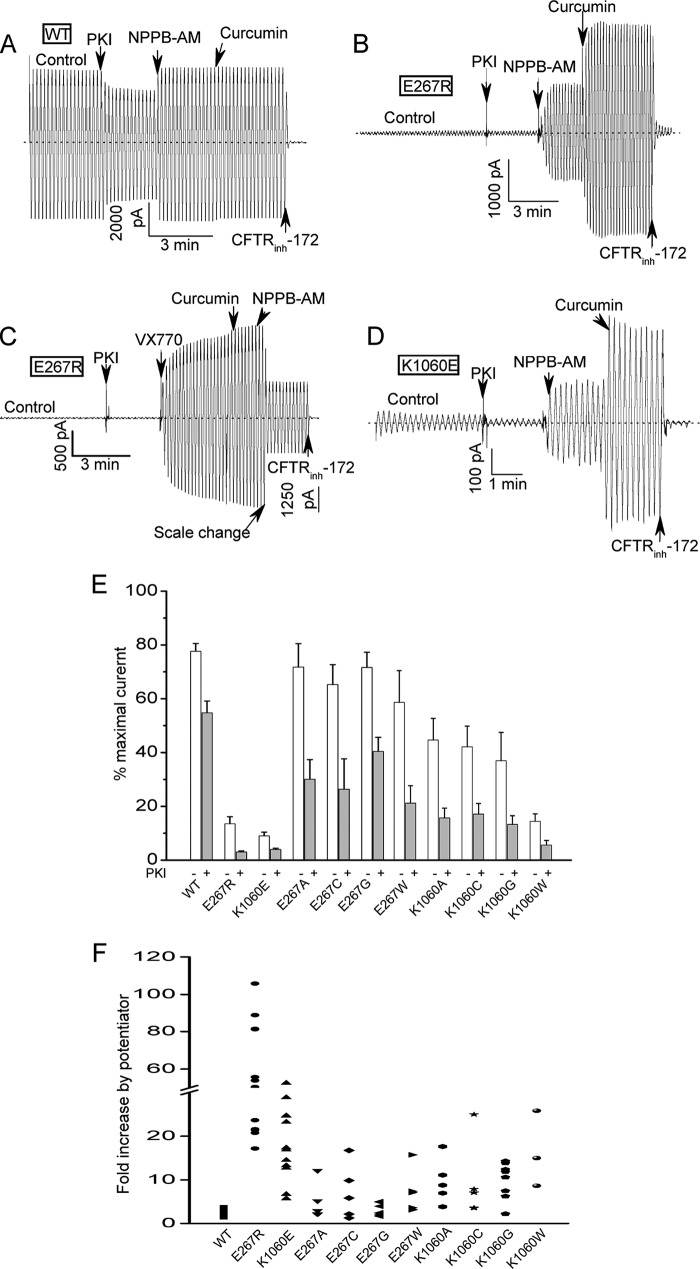
FIGURE 2.
Strong inhibition of CFTR channel activity by charge- reversal mutations at positions 267 and 1060. A, macroscopic current record for excised inside-out patch containing many (> 1000) wild type (WT) CFTR channels. Ramp protocol: ± 80 mV; 10 s time period. Dotted line shows zero current level. Control condition was 110 units/ml PKA and 1.5 mm Mg-ATP. Inhibitory PKA peptide (1.4 μg/ml PKI) was added to block further phosphorylation resulting in partial current deactivation due to partial dephosphorylation by membrane-associated phosphatases (12, 28). Two CFTR potentiators, NPPB-AM (10 μm) and curcumin (30 μm), and a CFTR inhibitor (20 μm CFTR-(inh)172) were added sequentially to the bath where indicated. B, macroscopic current record for patch containing many E267R-CFTR channels showing very small control current and very large activation by potentiators. Conditions were identical to panel A. C, macroscopic record showing that E267R-CFTR channels also are strongly stimulated by the FDA-approved potentiator, VX-770 (10 μm). D, K1060E-CFTR channels also exhibit reduced control currents and strong activation by potentiators. E, mean currents (± S.E.) measured at −80 mV before and after PKI addition for the indicated constructs. Currents were normalized to the maximal currents measured after the addition of NPBB-AM and curcumin. N ranges from 5 to 17. The charge-reversal mutations at positions 267 and 1060 strongly reduced the currents before and after PKI addition. Most of the neutral substitutions had modest effects on the control currents measured before PKI addition but nearly all reduced the normalized currents measured after PKI addition compared with WT-CFTR. For all mutants except E267G the relative currents after PKI addition were significantly less than for WT (p < 0.05) by unpaired t test. F, scatter plot showing the fold current stimulation by the addition of NPPB-AM and curcumin for the indicated constructs. Each symbol represents an individual experiment. Note the break in the Y-axis. Conditions were identical to panels A–E. Potentiators were added after PKI. The charge-reversal mutants were most strongly activated because of their very low control currents but nearly all of the neutral mutants also showed stronger relative stimulation by potentiator addition compared with WT-CFTR.