FIGURE 5.
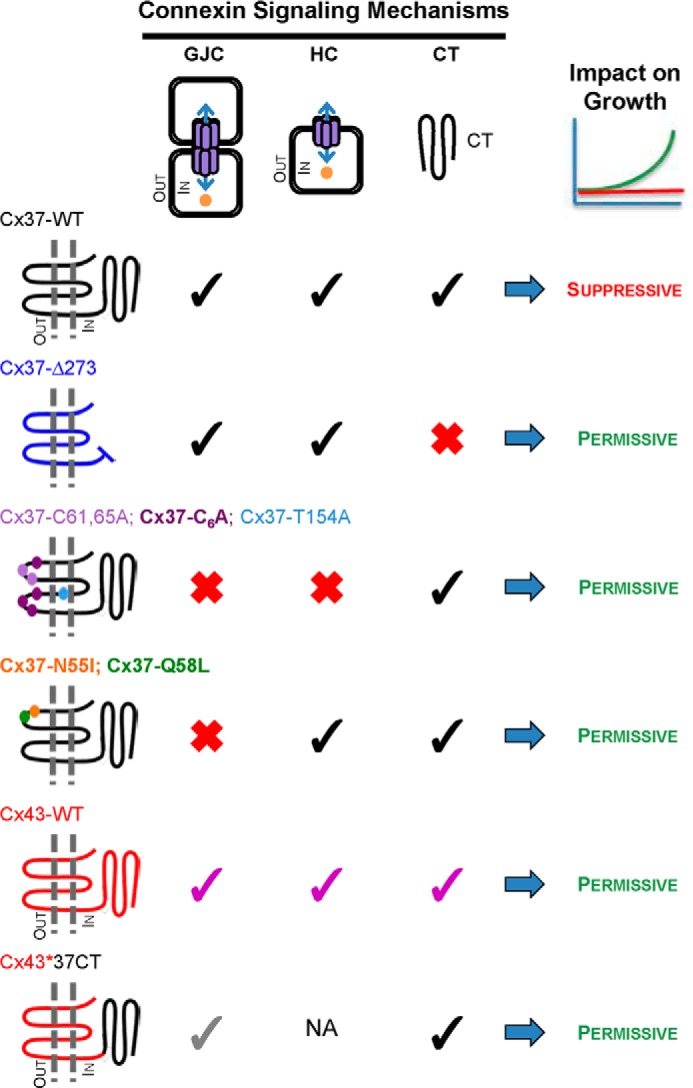
Connexin functions necessary for suppression of Rin cell proliferation. Growth-suppressive function of Cx37-WT could require functional (black checks) GJCs, HCs, or C terminus (CT), or a combination of these properties. The C terminus could influence growth through regulatory effects on channel function as well as via channel-independent mechanisms, such as through interactions with growth regulatory proteins. Truncated Cx37 (Cx37-Δ273) forms functional GJCs and HCs, but without its C terminus (red X), it fails to suppress the proliferation of Rin cells (10). Cx37-T154A (9), Cx37-C61A,C65A (11), and Cx37-C6A (present data) all retain their full-length C terminus, but none forms functional GJCs or HCs and all fail to suppress growth, indicating the necessity of channel function for growth suppression. Cx37-N55I and Cx37-Q58L fail to form functional GJCs, but retain functional HCs and their full-length C terminus, but nevertheless fail to suppress proliferation. Cx43 (purple checks) forms functional GJCs and HCs, although the properties of these channels differ from Cx37, and has a full-length C terminus with a different primary amino acid sequence from Cx37, but fails to suppress Rin cell proliferation (7). Rin cell proliferation is not suppressed by the Cx43*37CT chimera (where CT indicates C terminus) despite the presence of the Cx37 C terminus and formation of functional GJCs, albeit with unique properties (gray checks) (10, 26). NA: not available. Together, these results indicate that Cx37 exerts a growth-suppressive effect only when it is capable of all three functions, intercellular, transmembrane, and intracellular signaling, specifically those supported by the Cx37 sequence.
