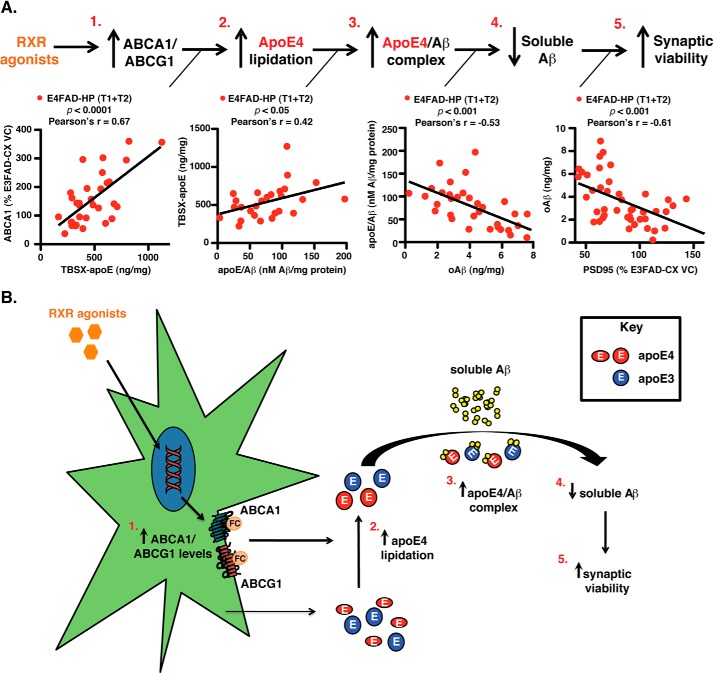
FIGURE 9.
Summary hypothesis, RXR agonists induce beneficial effects in the E4FAD-HP. A, data from this study support the hypothesis that in the E4FAD-HP, the short-term RXR agonist treatment (T1 and T2) is as follows: 1, increases ABCA1/G1 levels; 2, increases apoE4 lipoprotein association/lipidation (as ABCA1 and TBSX-apoE levels are positively correlated); 3, increases apoE4/Aβ complex levels (as TBSX-apoE and apoE4/Aβ complex levels are positively correlated); 4, decreases soluble Aβ levels (as oAβ and apoE4/Aβ complex levels are inversely correlated); and 5, improves synaptic viability (as oAβ and PSD95 levels are inversely correlated). Thus, RXR agonists address a loss-of-function associated with APOE4 and exacerbated by Aβ, i.e. lower apoE4 lipoprotein association/lipidation. B, schematic representation of the proposed hypothesis.