FIGURE 4.
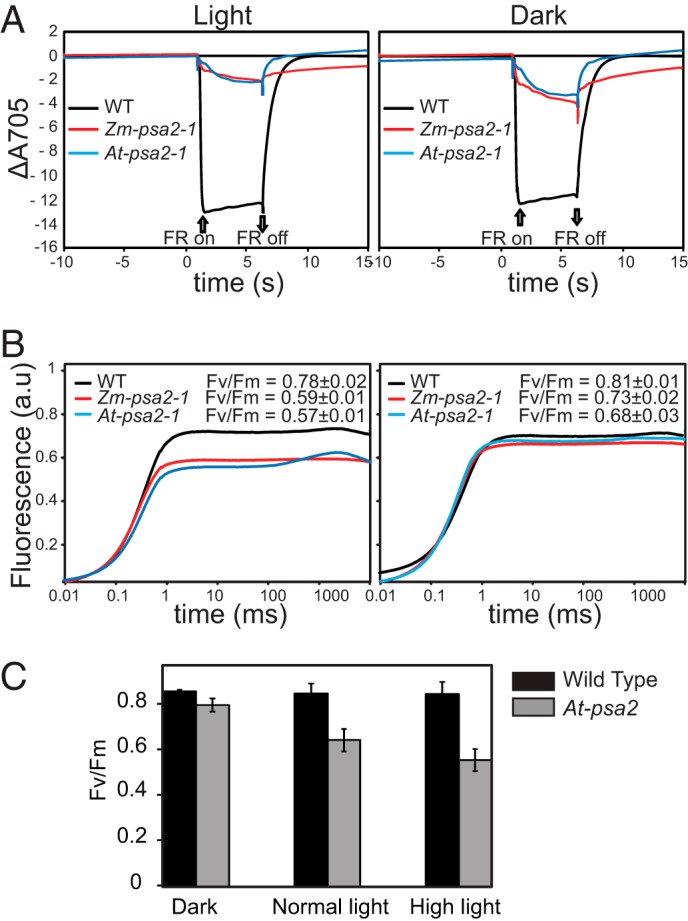
Spectroscopic characterization of PSI and PSII activity in psa2 mutants. A, PSI activity. The oxidation state of P700 was determined by measuring the absorbance at 705 nm after plants were illuminated with far-red light (720 nm). Plants of the indicated genotypes were monitored either during growth at normal photon flux density (120 μmol m−2 s−1) (left panel) or after 12 h in the dark (right panel). Leaves were soaked in 3-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-1,1-dimethylurea for 10 min prior to the measurements. The plants were dark-adapted for 20 min and then preilluminated with far-red light for 2 min prior to the measurements (64). Wild-type (WT) maize and Arabidopsis performed very similarly in this assay (not shown); only the Arabidopsis data are shown. B, PSII activity. Time-resolved fluorescence kinetics of chlorophyll a from plants of the indicated genotypes grown at normal photon flux density (left panel) or dark-adapted for 12 h are shown. Leaves were soaked in 3-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-1,1-dimethylurea for 10 min prior to the measurements. The leaves from the light-grown plants were dark-adapted for 20 min before the measurements. Wild-type (WT) maize and Arabidopsis performed very similarly in this assay (not shown). C, the ratio of variable to maximal chlorophyll fluorescence (Fv/Fm) measured in Arabidopsis plants adapted to dark (12 h), normal light (120 μmol of photons m−2 s−1), or high light (800 μmol of photons m−2 s−1 for 12 h). The plants were germinated and grown for 2 weeks under standard light conditions and then shifted to the indicated light conditions at the time of the normal dark to light transition. Readings were taken 12 h after the light shift. Error bars represent one S.D. (n = 8). FR, far-red; a.u., absorbance units.
