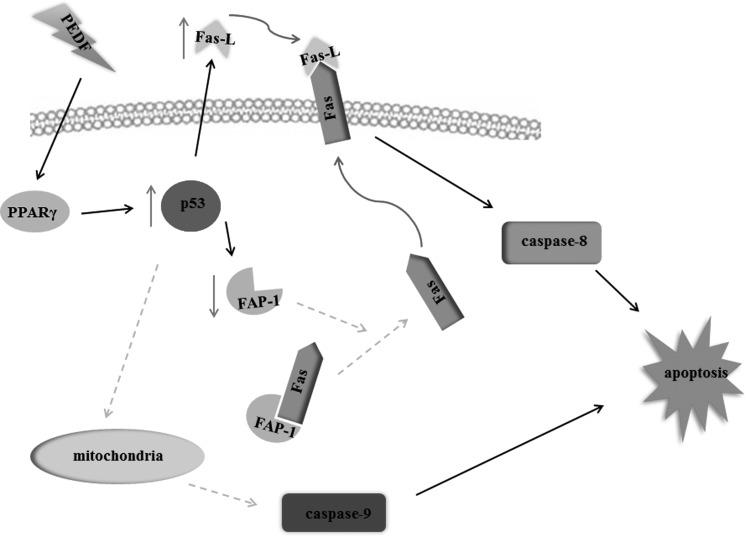
FIGURE 11.
Schematic of the underlying mechanism of PEDF-induced lung cancer cell apoptosis. In the presence of PEDF, PPARγ is up-regulated, and then p53 is activated. The activation of p53, on one hand, up-regulates Fas-L expression. One the other hand, the activation of p53 down-regulates FAP-1 expression and the interaction between FAP-1 and Fas. The FAP-1-free Fas transports onto the cytoplasmic membrane and binds with the increased Fas-L, which activates caspase 8 and, therefore, induces cell apoptosis. In addition, the activation of p53 might also initiate the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway, promote the cleavage of caspase 9, and, finally, trigger cell apoptosis.