FIGURE 1.
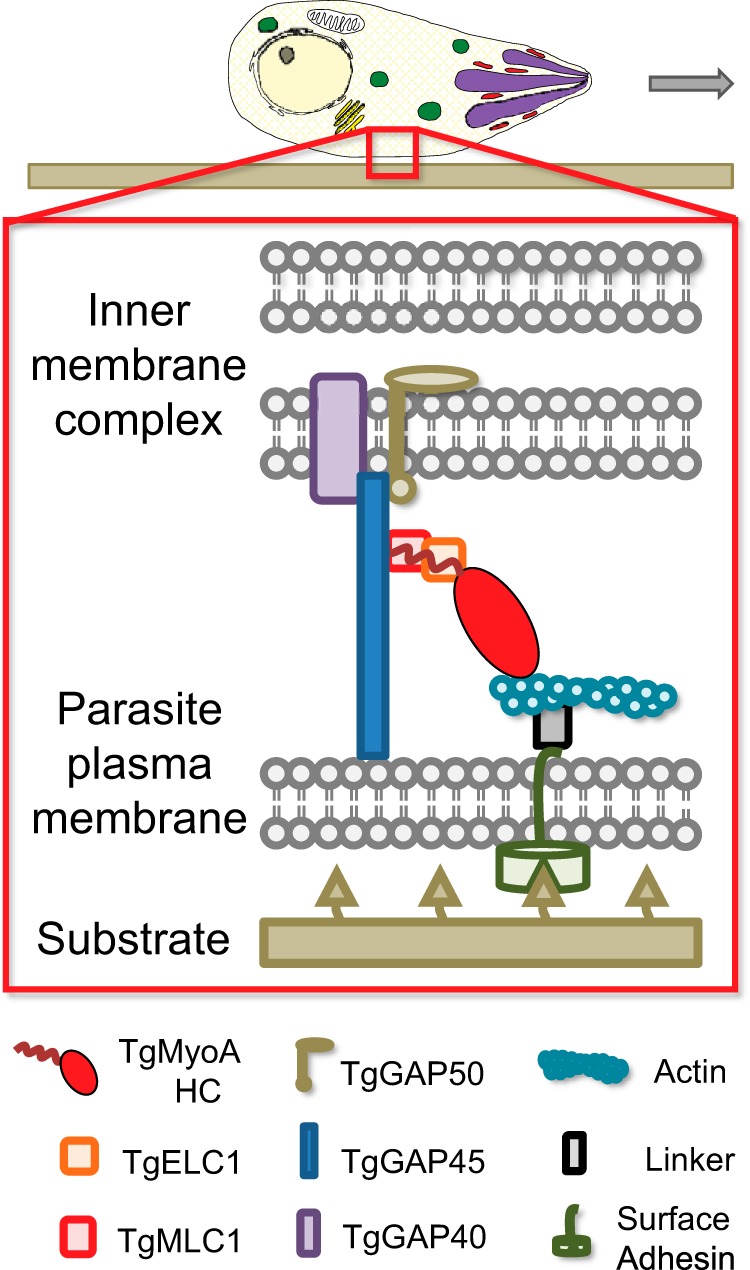
Schematic of T. gondii myosin motor complex. TgMyoA (i.e. TgMyoA heavy chain (HC) with its bound light chains TgMLC1 and TgELC1) and TgGAP45 are anchored to the IMC via transmembrane protein TgGAP50. This multiprotein complex is referred to as the myosin motor complex. Short actin filaments are located between the parasite plasma membrane and the IMC and are thought to be connected to ligands on the host cell surface through linker protein(s) that bind to the cytosolic tails of surface adhesins. TgMyoA (attached to the IMC) displaces the actin filaments (attached to the substrate), causing the parasite to move relative to the substrate. Note that alternative models of parasite motility are emerging (50, 51) in which TgMyoA plays a different but still important role in generating the force required for motility. The figure was adapted from Ref. 9.
