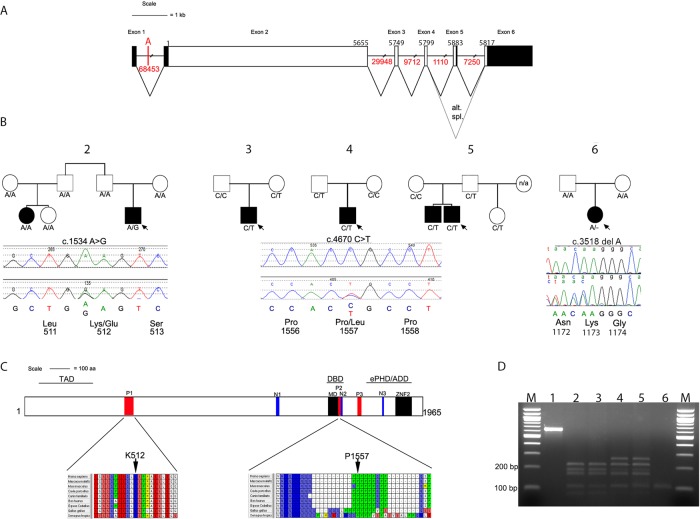
Figure 3.
TCF20 gene structure, identification of variants in ASD cases and their location within conserved domains. (A) Schematic representation of TCF20, exons are shown to scale with the coding sequence in white and untranslated regions filled in with black. There is an alternative stop codon in the alternatively spliced exon 5. The position of the first coding nucleotide is shown in exon 2, numbers above boxes indicate cDNA numbering at last nucleotides of exon boundaries or last nucleotide of stop codons; numbers in red below lines indicate intron sizes (not to scale). The location of breakpoint A that interrupts TCF20 23350 bp 5′ of exon 2 is also indicated. (B) Pedigrees of five families with variants of TCF20 that are either novel or enriched compared with control samples. Below each pedigree is a chromatogram showing the sequence change together with the amino acids encoded by the change and by adjacent codons. Black symbols indicate individuals with a clinical and research ASD diagnosis, the white symbol indicates people without clinical ASD; where broader autism phenotype data are available this is described in the text; n/a indicates that no DNA was available for analysis. Under each symbol, the status of that individual for the change found in the proband is shown. (C) Diagram representing the TCF20 protein with previously annotated domains: P1-P3, PEST domains; N1-N3, nuclear localisation signals; MD, minimal DNA binding domain; ZNF2, zinc finger domain. The three lines above the protein denote the following domains: TAD, transactivation domain; DBD, DNA binding domain and the ePHD/ADD domain.37 The lower panel shows the positions and conservation of amino acid residues predicted to be substituted in ASD pedigrees. The entire PEST1 and PEST2 sequences are shown with interspecies conservation in mammals, chicken and frog. (D) Analysis of cDNA amplification product compared with genomic (gDNA) from region containing c.3518delA mutation in family #6. Restriction digestion was performed with BslI, yielding product sizes (bp) of 215, 162, 145, 72, 1 in the absence of the mutation and 233, 215, 145, 1 in the presence of the mutation. Lanes numbered as follows: 1, undigested gDNA from proband; 2, mother's gDNA; 3, father's gDNA; 4, proband's gDNA; 5, proband's cDNA and 6, −RT control for proband's cDNA. Note similar relative intensities of mutant and non-mutant fragments in lanes 4 and 5, indicating lack of significant nonsense-mediated decay associated with the frameshifting mutation.