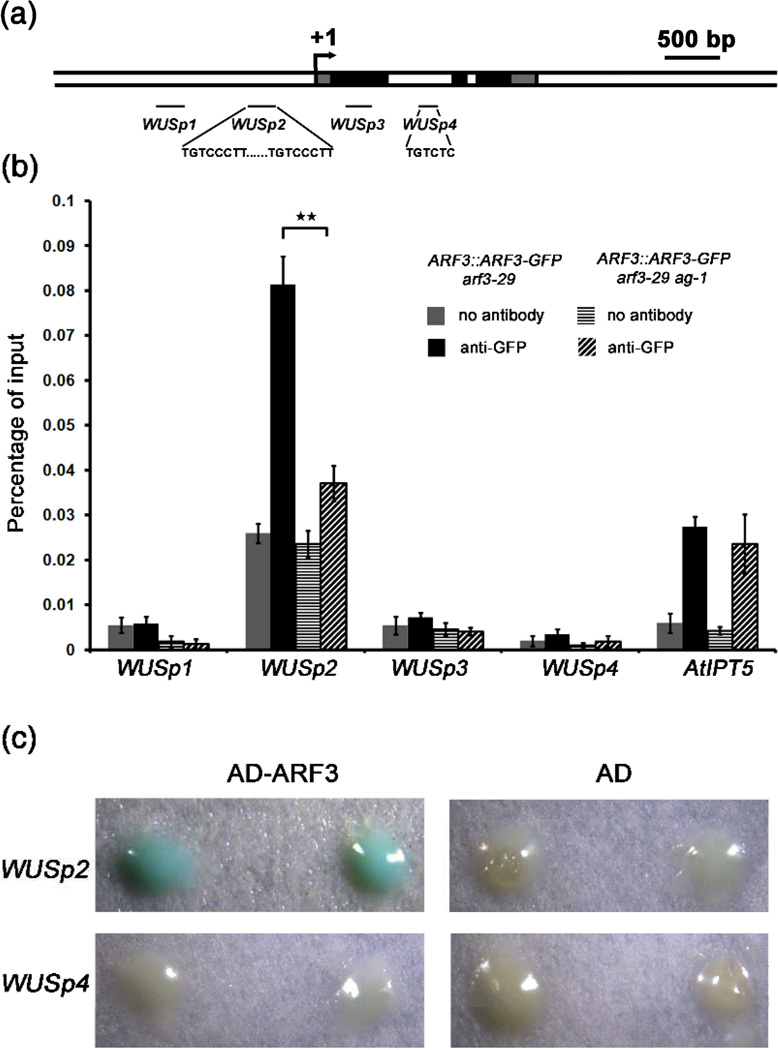
Figure 6. AG promotes the binding of ARF3 to the WUS locus in vivo.
(a) A diagram of the WUS genomic region with “+1” corresponding to the transcription start site. The gray, black and white rectangles represent the 5’ or 3’ untranslated regions, coding regions and introns or intergenic regions, respectively. The black lines indicate the regions examined in ChIP. The sequences of the putative ARF3 binding sites are also shown.
(b) ARF3 occupancy at WUS and atIPT5 as determined by ChIP-qPCR. Anti-GFP antibody was used for ChIP, and “no antibody” served as the negative control. Error bars represent SD calculated from four biological replicates. Statistically significant changes are indicated by ★★ (p-value < 0.01).
(c) Yeast one-hybrid analysis revealing the direct binding of ARF3 to WUSp2. Yeast strains containing WUSP2∷LacZ or WUSp4∷LacZ reporters were transformed with AD-ARF3 or AD vectors, respectively. Two independent transformants growing on selective medium (SD/-Leu) were selected for β-galactosidase assay.