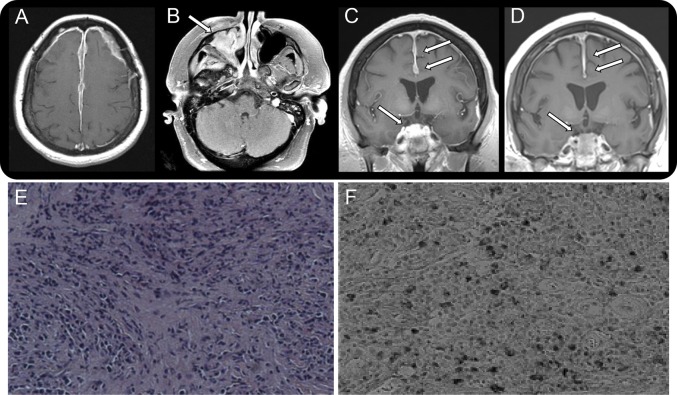
Figure. Radiologic and histopathologic findings in a patient with IgG4-related intracranial hypertrophic pachymeningitis.
(A–D) Radiologic findings over 10 years. (A) Brain MRI from 2003 with and without contrast: axial T1 postcontrast sequence shows extensive dural enhancement along the falx and bilateral frontotemporal convexities. (B) Axial T1 postcontrast sequence from 2011 shows enhancement in the right maxillary sinus. (C) Before treatment with rituximab: coronal T1 postcontrast sequence from 2013 shows diffuse dural enhancement in both frontotemporal convexities and nodular enhancement in the right suprasellar region that extends into the clivus. (D) After treatment with rituximab: coronal T1 postcontrast sequence from 2014 shows significant reduction of the dural enhancement in both frontotemporal convexities and nodular enhancement/mass effect in the right suprasellar region. (E, F) Histopathologic features of dura from middle cranial fossa biopsy. (E) Dense fibrosis admixed with abundant inflammatory cell infiltration (hematoxylin & eosin staining, ×100). (F) Abundant IgG4-positive plasma cell infiltration (IgG4 staining, ×200).