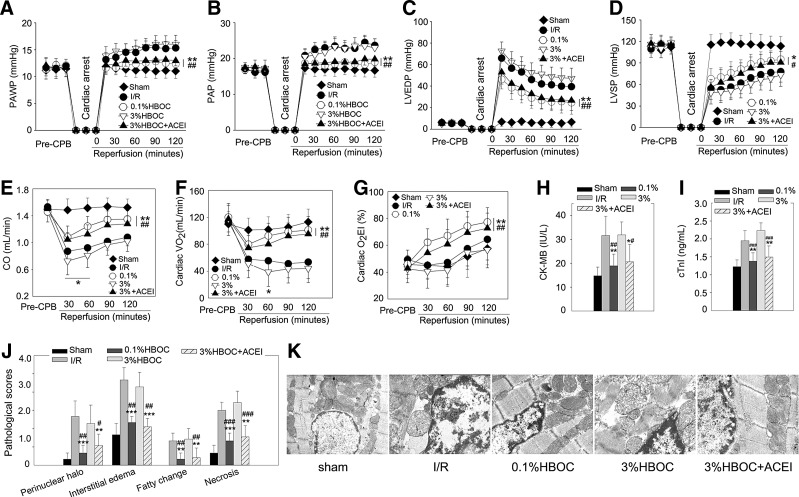
FIG. 1.
Cardiac I/R injury exacerbated by high-dose HBOC is reduced by captopril. The cardiac functional parameters, including PAWP (A), PAP (B), LVEDP (C), LVSP (D), CO (E), and cardiac VO2 (F) and O2EI (G), of dog hearts during CPB study (n=6). Total CK-MB (H) and cTnI (I) releases after 2-h reperfusion (n=6). (J) Pathological scores for acute myocardial necrosis, interstitial edema, perinuclear halo, and fatty changes (n=5). (K) Structural mitochondrial changes of dog LV tissues assessed by transmission electron microscopy (n=5, five fields for each specimen). Original magnification×12,000. Values are presented as mean±SD. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, and ***p<0.001 versus the I/R group; #p<0.05, ##p<0.01, and ###p<0.001 versus the 3%HBOC group. ACEI in the figure indicates ACE inhibitor captopril. CO, cardiac output; CK-MB, creatine kinase-MB; CPB, cardiopulmonary bypass; HBOC, hemoglobin-based oxygen carriers; I/R, ischemia/reperfusion; LVEDP, left ventricular end-diastolic pressure; LVSP, left ventricular systolic pressure; O2EI, O2 extraction index; PAP, pulmonary arterial pressure; PAWP, pulmonary artery wedge pressure; VO2, cardiac O2 consumption.