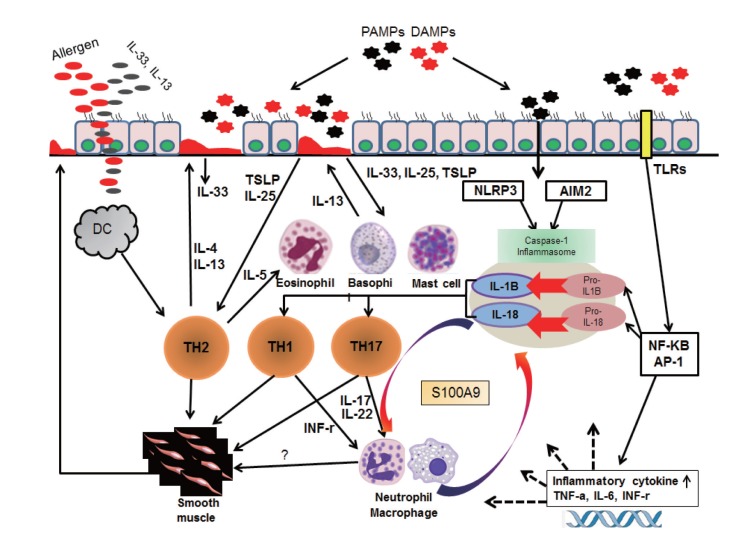
Fig. 4.
Interaction of inflammasome activation and S100A9 in neutrophilic inflammation of asthma. Asthma is characterized by the airway infiltration of eosinophils and mast cells. IgE-dependent asthma is under the influence of the T helper 2 (Th2)-cytokines (interleukin [IL] 4, IL-5, and IL-13) generated by Th2-type cells. In T-cell independent manner, TSLP and IL-33 released from the activated epithelium stimulates mast cells to release the Th2-type effector cytokines. These can attract and activate eosinophils and mast cells. As another pathway, PAMPs and DAMPs including offending allergens induces nuclear factor (NF)-κB activation via Toll-like receptor (TLR) and concurrent inflammasome activation via nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain (NOD) receptors; subsequent activation of Th17 cells to regulate both neutrophilic and macrophage inflammation. TSLP, thymic stromal lymphopoietin, pathogen-associated molecular patterns; NLRP3, NOD-like receptor family, pyrin domain containing 3 activation; PAMP, damage-associated molecular patterns; DAMP, danger-associated molecular pattern; INF, interferon; TNF, tumor-necrosis factor.