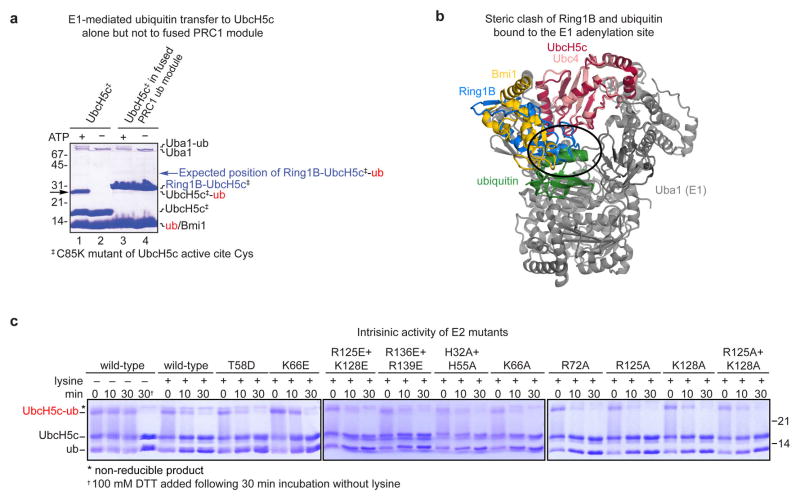
Extended Data Figure 2. Characterization of fused and unfused UbcH5c.
a, Coomassie stained gel of E1-mediated ubiquitin transfer to UbcH5c Cys85Lys mutant (UbcH5c‡) alone and in the context of the fused PRC1 ubiquitylation module. Ubiquitin is transferred by the E1 Uba1 to the UbcH5c mutant in an ATP dependent manner, black arrow (lanes 1 and 2). No ubiquitin transfer to the fused PRC1 ubiquitylation module is observed (lanes 3 and 4, expected band position for Ring1B-UbcH5c-ubiquitin conjugate indicated by a blue arrow). The Cys85Lys mutant was used to assist in visualization of the UbcH5c-ubiquitin stable isopeptide conjugates. b, Ring1B of the fused PRC1 ubiquitylation module (blue) clashes with ubiquitin in the E1 Uba1 adenylation site (green). Alignment of UbH5c subunit of PRC1 ubiquitylation module22 (PDB ID 3RPG) to Ubc4 in Ubc4/Uba1/ubiquitin structure24 (PDB ID 4II2). Ubc4 and Uba1 are shown pink and grey, respectively. c, Intrisic activity of wild-type and mutant UbcH5c enzymes. Time-course of UbcH5c-ubiquitin thioester aminolysis upon lysine addition. Reactions quenched with non-reducing loading buffer unless 100 mM DTT addition is indicated (†). Asterisk denotes a non-reducible product.