Figure 1. Aryl iodide saponin 6 exhibits potent adjuvant activity and low toxicity in a preclinical mouse vaccination model.
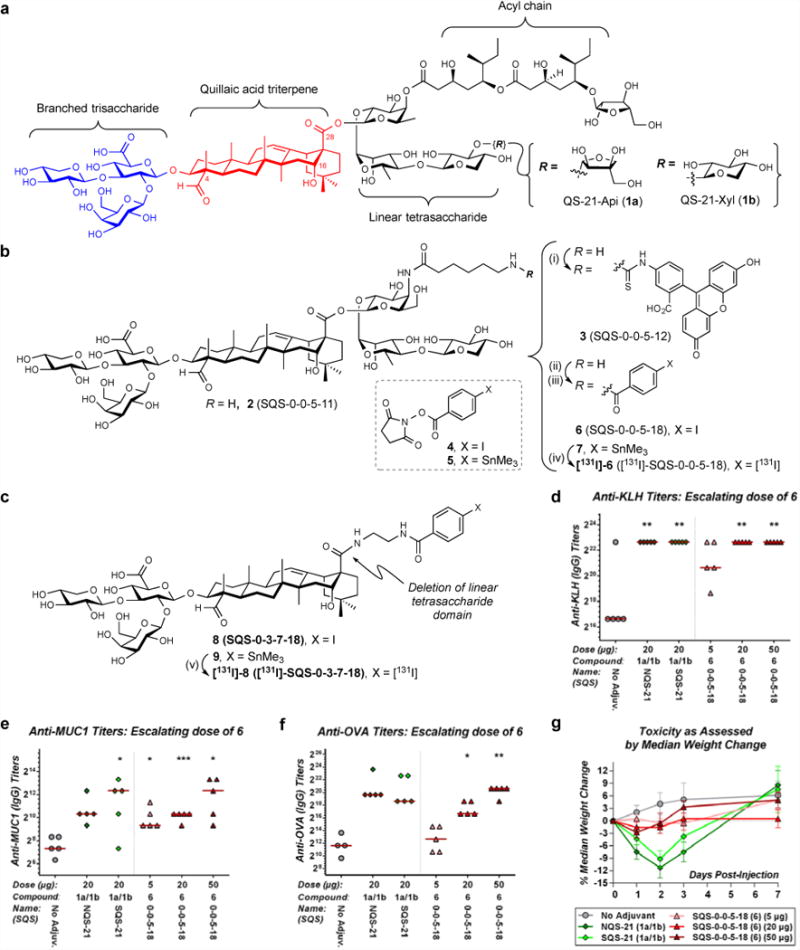
(a) Structure of QS-21 and its four key structural domains. (b) Synthesis of aryl iodide saponins 6 (SQS-0-0-5-18) and [131I]-6: (i) FITC, Et3N, DMF, 21 °C, 2 h, 75%; (ii) 4, Et3N, DMF, 21 °C, 1 h, 52%; (iii) 5, Et3N, DMF, 21 °C, 1 h, 75%; (iv) [131I]-NaI, Chloramine-T, MeOH, 21 °C, 1 min, >50%. (c) Structure of adjuvant-attenuated negative control saponin 8 (SQS-0-3-7-18) and synthesis of [131I]-8: (v) [131I]-NaI, Chloramine-T, MeOH, 21 °C, 1 min, >50%. Biological evaluation of aryl iodide saponin 6 (SQS-0-0-5-18) with three-component vaccine for (d) anti-KLH titers (IgG), (e) anti-MUC1 titers (IgG), and (f) anti-OVA titers (IgG) indicating potent adjuvant activity comparable to natural and synthetic QS-21 (compare 20 μg doses); horizontal bars indicate median titers; statistical significance compared to no-adjuvant control: * = p ≤ 0.05, ** = p < 0.01, *** = p < 0.001. (g) Toxicity assessment based on median percent weight loss, indicating low toxicity of 6 (SQS-0-0-5-18); error bars indicate maximum and minimum values for five mice.
