Figure 5. Caulophyllogenin derivative 19 and echinocystic acid derivative 20, which lack the C4-aldehyde substituent but retain the C16-alcohol in the triterpene domain of QS-21, exhibit potent adjuvant activity and no toxicity in a preclinical mouse vaccination model.
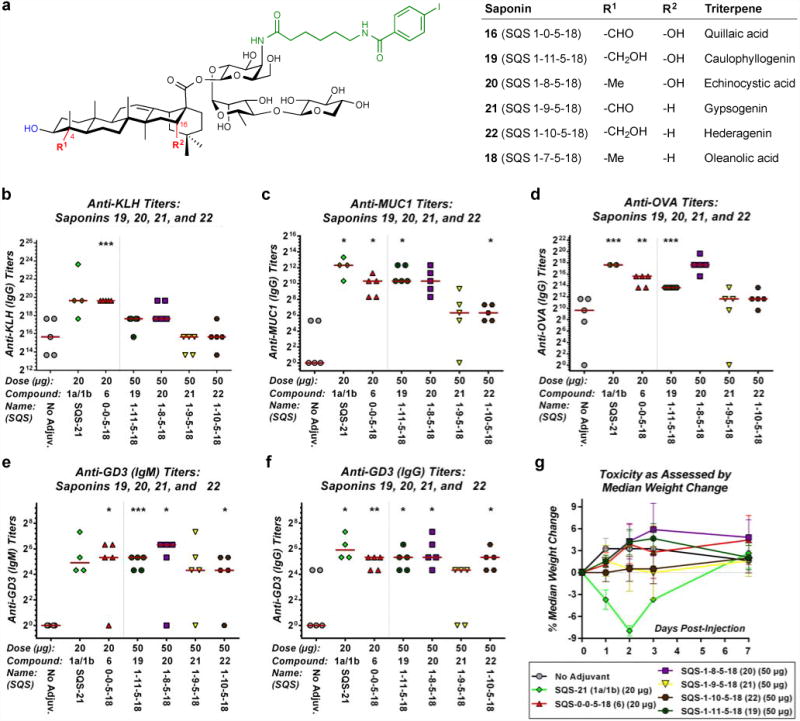
(a) Structures of saponin variants 19–22 with modifications at the C4-aldehyde substituent and C16-alcohol of the triterpene domain of QS-21. Biological evaluation of triterpene variants 19–22 with a four-component vaccine (MUC1-KLH, OVA, GD3-KLH) for (b) anti-KLH (IgG), (c) anti-MUC1 (IgG), (d) anti-OVA (IgG), (e) anti-GD3 (IgM), and (f) anti-GD3 (IgG) titers, indicating that the C4-aldehyde substituent is not required adjuvant activity (19, 20) while removal of the C16-alcohol attenuates activity (21, 22) (see Supplementary Fig. 10 for full data with both 20 and 50 μg doses); horizontal bars indicate median titers; statistical significance compared to no-adjuvant control: * = p ≤ 0.05, ** = p < 0.01, *** = p < 0.001. (f) Toxicity assessment based on median percent weight loss, indicating lack of toxicity of 19–22; error bars indicate maximum and minimum values for five mice.
