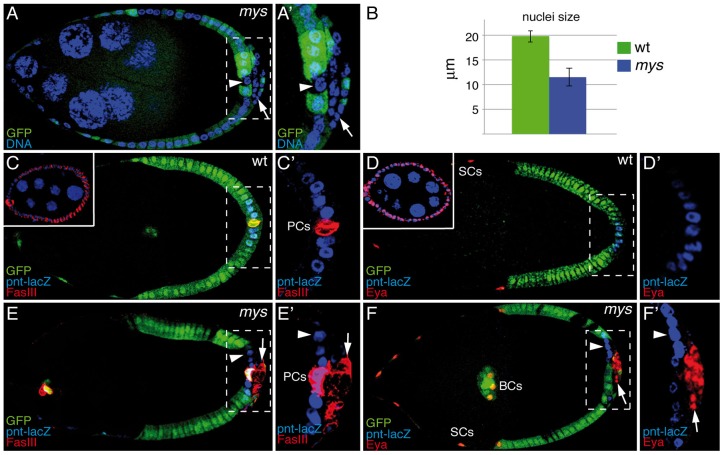
Fig. 1.
Integrins regulate PFC differentiation. (A) An S9 mosaic egg chamber carrying mys mutant clones (GFP−) was stained for anti-GFP and the DNA marker TO-PRO-3 (blue). Although mys PFCs in contact with the germline (GFP−, arrowhead) have normal nuclear size, the nuclear size of those located in ectopic layers (GFP−, arrow) is smaller than that of surrounding wild-type (wt) cells (GFP+). (B) Quantification of the nuclear size. Data show the mean±s.d. (C–F) S9–S10 wild-type and mosaic egg chambers carrying mys mutant clones expressing the posterior cell fate marker pnt-lacZ, and stained with anti-GFP (green), anti-β-galactosidase (C–F; blue), anti-FasIII (C,E; red) and anti-Eya (D,F; red). In S9–S10 wild-type egg chambers, FasIII (C) and Eya (D) are restricted to polar cells (PCs; FasIII) or to border cells (BCs) and stretched cells (SCs; Eya), whereas pnt-lacZ is specifically expressed in PFCs from S6 onwards (C,D). However, in mys PFCs located in ectopic layers (GFP−, arrow), FasIII (E) and Eya (F) are maintained, whereas pnt-lacZ is inhibited (E,F). mys PFCs in contact with the germline (GFP−, arrowhead in E,F) behave as wild-type follicle cells. Upper-left panels in C and D show the expression of FasIII and Eya in S4 egg chambers, respectively. Anterior is to the left in all figures. (A′–F′) Magnifications of the white boxes in A–F, respectively.