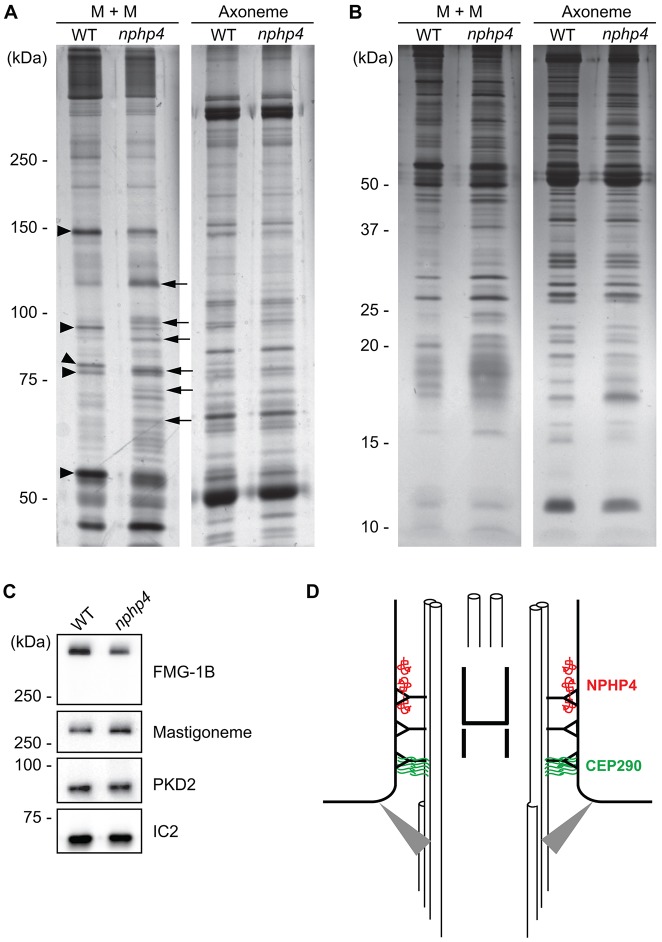
Fig. 7.
Flagella of nphp4 cells have abnormal protein composition. 6% (A) or 12% (B) SDS-polyacrylamide gels were used to compare wild-type (WT) versus nphp4 membrane-plus-matrix (M+M) and axonemal fractions. Arrowheads indicate some proteins that decreased in amount in the nphp4 membrane-plus-matrix fraction; arrows indicate some proteins that increased in amount in the mutant flagella. (C) Western blot of isolated wild-type and nphp4 flagella probed with antibodies against FMG-1B, the mastigoneme protein and PKD2. The outer arm dynein intermediate chain IC2 served as a loading control. (D) Diagram illustrating the distribution of NPHP4 and CEP290 in the transition zone. NPHP4 (red) is located in close association with the membrane at the distal end of the transition zone. CEP290 (green) is located in the space between the doublet microtubules and membrane at the proximal end of the transition zone. Gray triangles represent transition fibers connecting the basal body to the plasma membrane.