Figure 2. The initiation and maintenance of osmotically evoked hypertrophy depends upon cell firing and Ca2+ influx and involves exocytotic fusion.
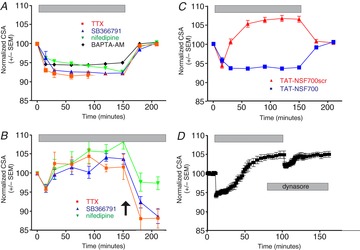
A, hypertrophy is prevented by treatment with tetrodotoxin (“TTX”; 0.2 μm; n = 24), SB336791 (1.5 μm; n = 26), nifedipine (10 μm; n = 27), or BAPTA-AM (10 μm; n = 20). B, hypertrophy is reversed in hypertonic saline by application (at arrow) of TTX (0.2 μm; n = 6), SB355791 (1.5 μm; n = 7), or nifedipine (10 μm; n = 7). C, hypertrophy is prevented by administration of the cell-permeant peptide TAT-NSF700 (n = 57), which blocks SNARE-mediated exocytotic fusion, but not the scrambled version of the peptide (TAT-NSF700scr; n = 19). D, the administration of dynasore (80 μm), an inhibitor of dynamin-mediated endocytosis, inhibits recovery from osmotically evoked hypertrophy (n = 10).
