Figure 9. Presynaptic inhibition of AC activity blocked the inhibitory effects of prior D1R activation on the LY379268-induced depotentiation of LTP following 5× HFS.
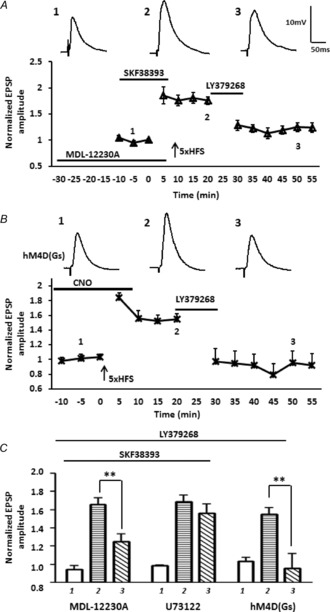
A, bath application of the membrane-permeable AC inhibitor, MDL-12230A (30 μm, n = 5), significantly reduced the ability of prior activation of D1Rs to attenuate LY379268-induced depotentiation of the eEPSP amplitude. B, enhancing postsynaptic AC levels by activating DREADD rM3D Gαs-coupled receptors in BLA principal neurons with exogenous CNO application during baseline and 5× HFS failed to attenuate LY379268-induced depotentiation of LTP (n = 5). C, bar chart illustrating the group effect of three different drug treatments on the magnitude of LTP before (1) and after (2, and 3) LTP induction. MDL-12230A significantly attenuated the effect of prior SKF38393 application on LY379268-induced depotentiation. Application of the PLC inhibitor U73122 (10 μm, n = 5) failed to block the SKF38393-mediated attenuation of LY379268-induced depotentiation. Selectively enhancing postsynaptic AC levels with Gs-coupled DREADDs failed to attenuate the LY379268-induced depotentiation of LTP. **P < 0.01. Error bars show ± SEM. Upper traces in A and B are representative EPSPs evoked at time points 1, 2 and 3.
