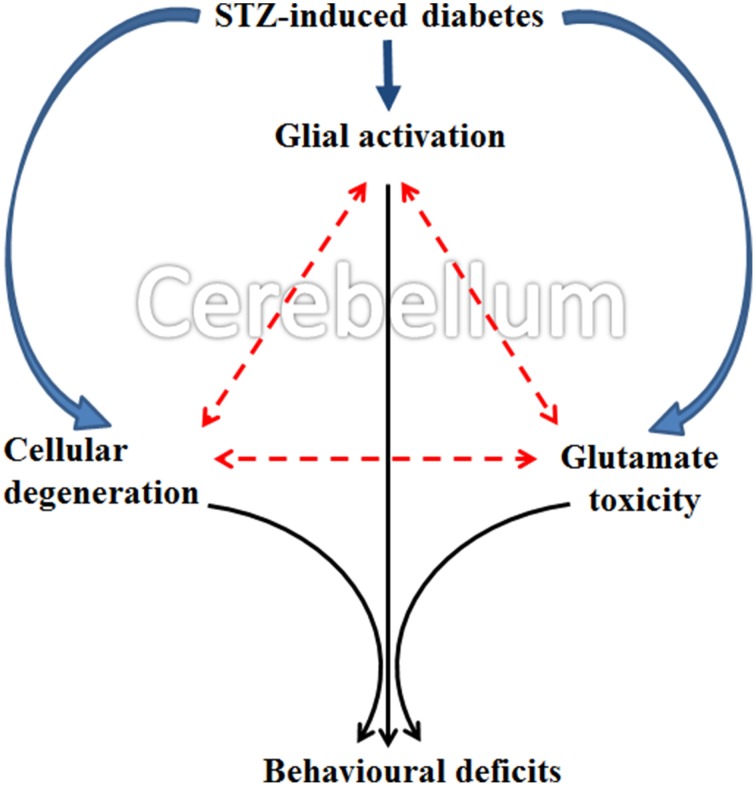
Figure 12.
Schematic representation showing possible occurrence of events in cerebellum following STZ-induced diabetes. Diabetes simultaneously induce glial activation, cellular degeneration and glutamate toxicity in cerebellum and the subsequent triangular associative interplay between these three factors resulted in motor deficits following diabetes.