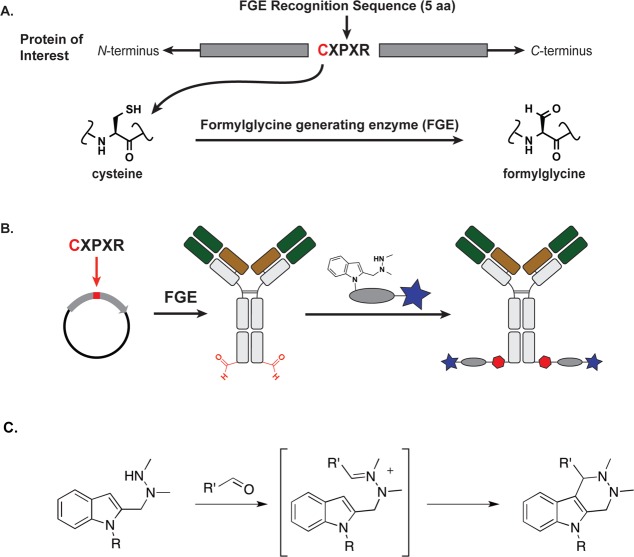
Figure 1.
Aldehyde tag coupled with HIPS chemistry yields site-specifically modified antibodies carrying a payload attached through a stable C–C bond. (A) A formylglycine-generating enzyme (FGE) recognition sequence is inserted at the desired location along the antibody backbone using standard molecular biology techniques. Upon expression, FGE, which is endogenous to eukaryotic cells, catalyzes the conversion of the Cys within the consensus sequence to a formylglycine residue (fGly). (B) Antibodies carrying aldehyde moieties (in red, 2 per antibody) are reacted with a Hydrazino-iso-Pictet-Spengler (HIPS) linker and payload to generate a site-specifically conjugated ADC. (C) The HIPS chemistry proceeds through an intermediate hydrazonium ion followed by intramolecular alkylation with a nucleophilic indole to generate a stable C–C bond.