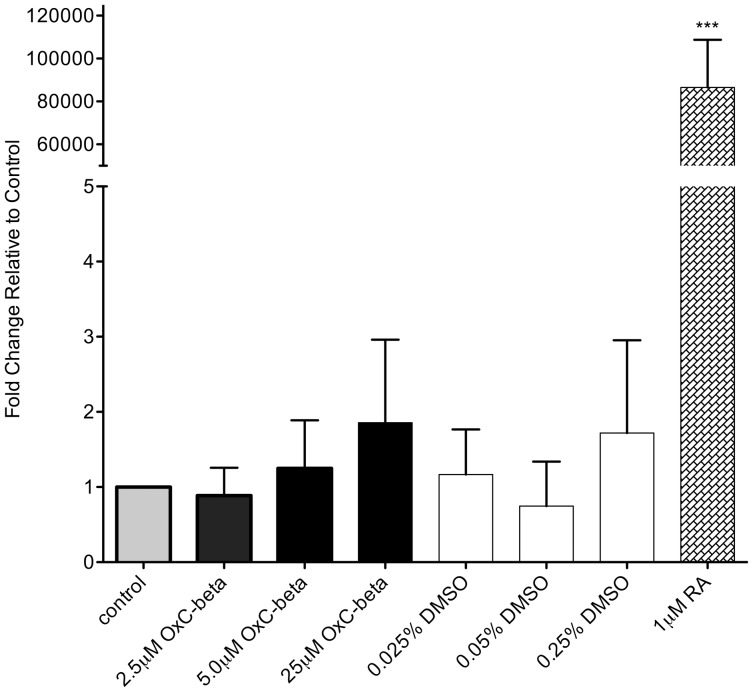
Figure 4. Effect of OxC-beta treatment on CYP26A gene expression in MCF-7 cells.
Cells were incubated in the presence of the indicated concentrations of OxC-beta or vehicle control for 24 hours. For vehicle controls the concentrations of DMSO used were equivalent to the concentration of DMSO in the OxC-beta treatment groups, i.e., control groups labeled as 0.025%, 0.05% and 0.25% DMSO had the same DMSO concentration (v/v) as was used in the 2.5 µM, 5.0 µM and 25 µM OxC-beta treatment groups, respectively. Untreated cells were used as negative controls and cells treated with 1.0 µM of all trans retinoic acid (RA) served as positive controls. CYP26A gene expression was measured relative to β-actin using quantitative real-time PCR with the two standard curve method. Bars represent the mean ratio of CYP26A expression relative to β-actin from 4 separate experiments. Error bars represent the standard error of the mean. One-way ANOVA with Tukey’s test for multiple comparisons indicated no significant difference in relative CYP26A expression between cells treated with OxC-beta, DMSO, or untreated control cells. Treatment with 1.0 µM RA induced a significant increase in CYP26A gene expression compared to all other treatment groups. CYP26A expression ratios are shown calibrated to untreated control cells. *** p<0.001.