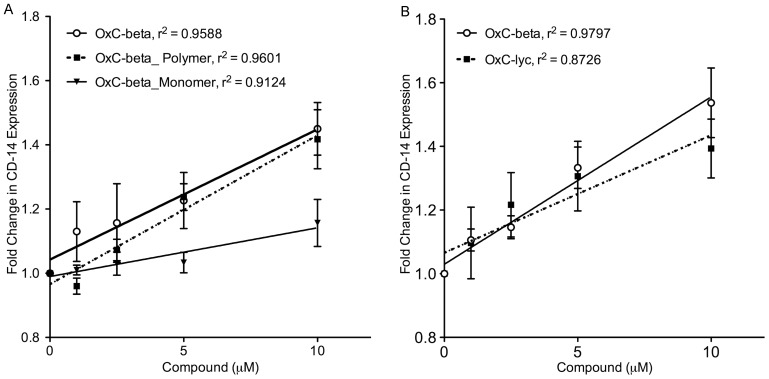
Figure 5. Determination of activities relative to OxC-beta of (A) OxC-beta polymer and monomer fractions, and (B) oxidized lycopene (OxC-lyc), using a CD14 receptor expression assay.
THP-1 cells were treated for 24 hours with the indicated concentrations of compounds. CD14 expression was quantified using FACS analysis. The effect of each compound is shown relative to untreated cells. Points represent the mean and standard error from three separate experiments. (A) Correlation analysis indicates a significant dose effect for each compound on CD14 expression with p-values of 0.0036 for OxC-beta, 0.0034 for the polymer, and 0.0113 for the monomer. Comparison of the relative activity of each compound indicates that the monomer is significantly less active than the polymer (p<0.001) and OxC-beta (p<0.01) while there is no significant difference between the activities of the polymer and OxC-beta. The apparent activity of the monomer may be due to the presence of residual polymers that could not be completely removed from the monomer fraction. (B) OxC-lyc also had a significant dose effect on CD14 surface content (p = 0.020) that was not significantly different from the effect of OxC-beta.