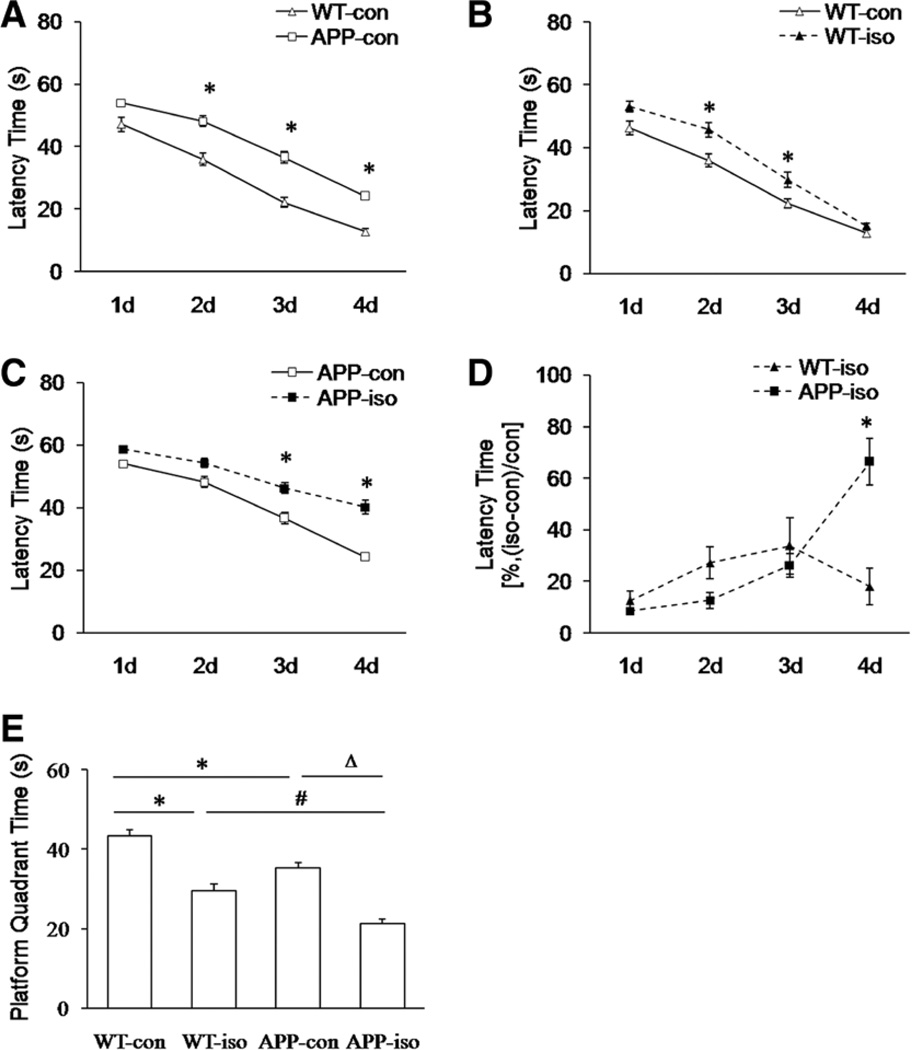
Figure 2.
The effect of isoflurane (iso) exposure on spatial learning and memory in both wild-type (WT) and transgenic amyloid precursor protein 695 (APP695) mice. All mice in iso-treated groups received 1 MAC of iso for 4 hours. A, During 4-day training period, the latency times in APP695 mice (APP-con) were significantly longer than those in WT mice (WT-con) before iso exposure (n = 10 per group, *P = 0.0003 for day 2, *P < 0.0001 for days 3 and 4 versus WT-con group). B, In isotreated WT mice (WT-iso), the latency times during 4-day training period were significantly increased compared with the control WT mice (n = 10 per group, *P = 0.005 for day 2 and *P = 0.002 for day 3 versus WT-con group). C, In iso-treated APP695 mice (APP-iso), the latency times during 4-day training period were significantly increased compared with the control APP695 mice (n = 10 per group, *P = 0.001 for day 3 and *P < 0.0001 for day 4 versus APP-con group). D, The data from iso exposure groups were normalized with their control (con) groups and expressed as percentage of latency time (%, [iso − con]/con). During 4-day training period, the latency times in APP695 mice were significantly longer than those in WT mice on day 4 after iso exposure (n = 10 per group *P = 0.0005 versus WT-iso group). E, Iso exposure significantly reduced platform quadrant times in both types of mice (n = 10 per group, *P < 0.0001 versus WT-con group and ΔP < 0.0001 versus APP-con group). Compared with WT mice, the transgenic APP695 mice displayed worse spatial memory before and after iso exposure (n = 10 per group, *P = 0.001 versus WT-con group and #P = 0.009 versus WT-iso group).