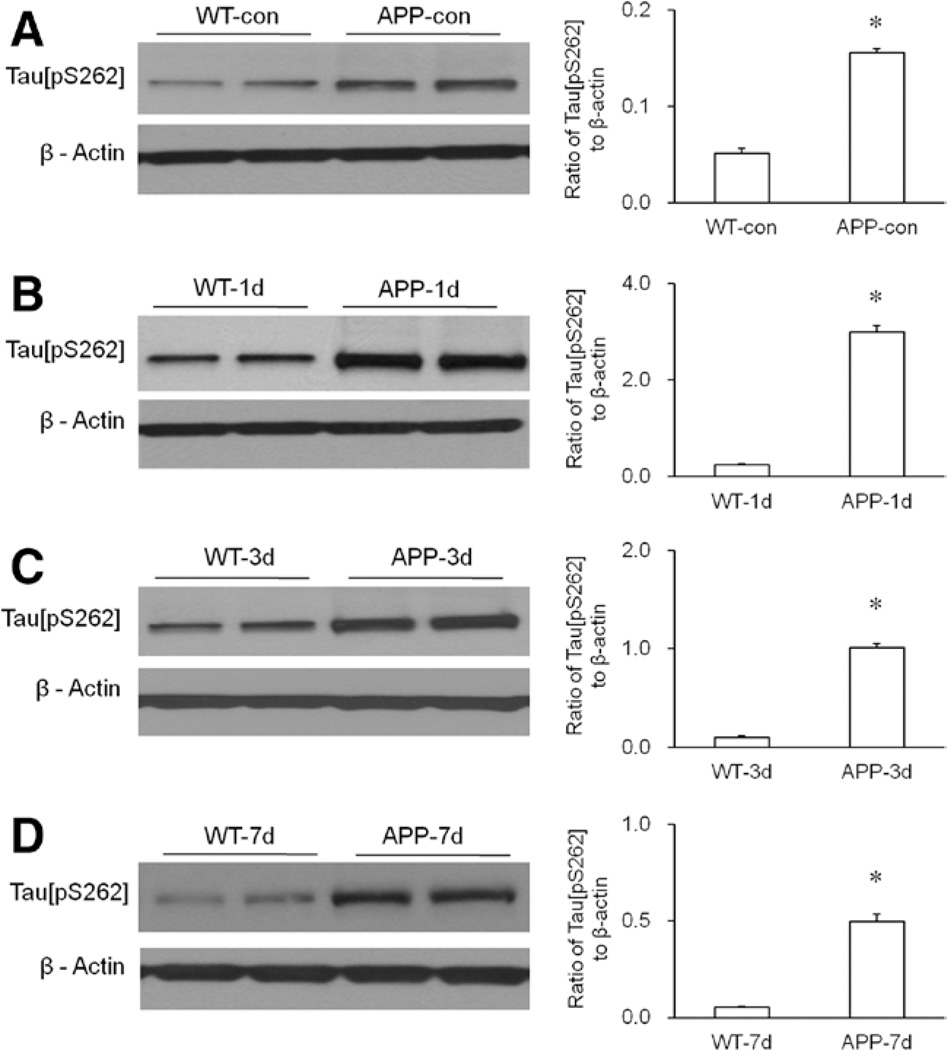
Figure 4.
Enhanced phosphorylation of hippocampal tau protein in the transgenic APP695 mice. A, Compared with wild-type (WT) mice, the amyloid precursor protein 695 (APP695) mice showed increased hippocampal tau[pS262] in normal condition. Statistical analysis indicated that the level of hippocampal tau[pS262] in the APP695 mice was significantly higher than that in WT mice (n = 6 per group, *P < 0.0001 versus WT-con group). B, Compared with WT mice, the APP695 mice showed increased hippocampal tau[pS262] on day 1 (APP-1d) after isoflurane exposure. Statistical analysis indicated that the level of hippocampal tau[pS262] in the APP695 mice was significantly higher than that in WT mice (n = 6 per group, *P < 0.0001 versus WT mice on day 1 [WT-1d] group). C, Compared with WT mice, the APP695 mice showed increased hippocampal tau[pS262] on day 3 (APP-3d) after isoflurane exposure. Statistical analysis indicated that the level of hippocampal tau[pS262] in the APP695 mice was significantly higher than that in WT mice (n = 6 per group, *P < 0.0001 versus WT-3d group). D, Compared with WT mice, the APP695 mice showed increased hippocampal tau[pS262] on day 7 (APP-7d) after isoflurane exposure. Statistical analysis indicated that the level of hippocampal tau[pS262] in the APP695 mice was significantly higher than that in WT mice (n = 6 per group, *P < 0.0001 versus WT-7d group). β-Actin served as a loading control for all Western blotting experiments.