FIG. 3.
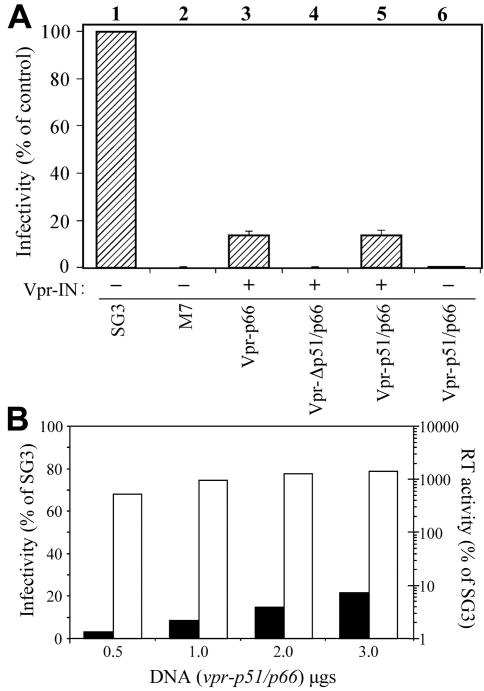
trans-complementation analysis of RT-IN-deficient virus. (A) Analysis of infectivity. Transfection-derived viruses were analyzed for infectivity using the TZM-bl reporter cell line as described in Materials and Methods. Infectivity is expressed as a percentage of the wild-type virus control. Viruses were derived from 293T cells with (+) or without (−) cotransfection of vpr-IN. The results of three independent experiments are shown. (B) Analysis of heterodimeric trans-RT activity. Increasing DNA concentrations of vpr-p51/p66 (ranging from 0.5 to 3.0 μg) were transfected into 293T cells together with a constant amount of M7 and vpr-IN. Culture supernatants were collected and treated as described in Materials and Methods. The transfection-derived virions were analyzed for infectivity using the TZM-bl reporter cell line (black bars) and for RT activity using the chemiluminescent RT assay (Roche) (white bars). Results are expressed as a percentage relative to an equal amount of wild-type SG3 virus.
