FIG. 1.
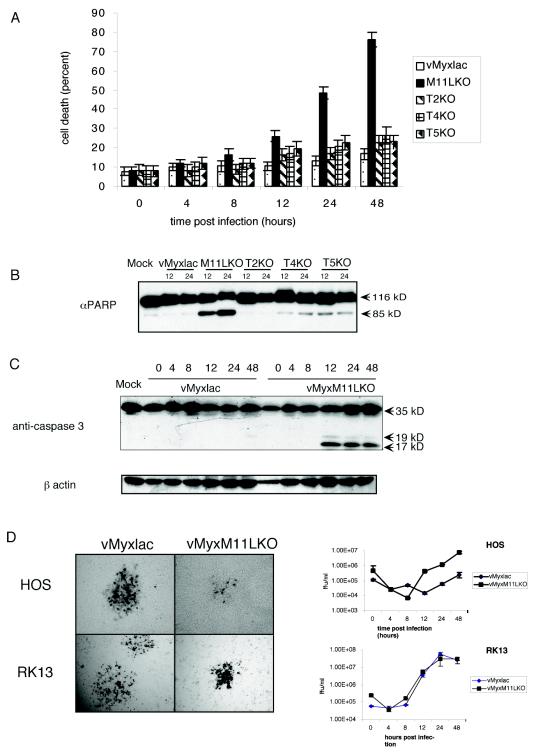
Myxoma virus infection of HOS cells blocks apoptosis. (A) Determination of cell death of HOS cells following infection with vMyxlac or the deletion mutant vMyxM-T2KO, vMyxM-T4KO, vMyxM-T5KO, or vMyxM11LKO (MOI, 5). At various times postinfection, the cells were stained with trypan blue, and the percentage of blue cells within the total cell population was determined. Values in the graph represent four replicates of 300 cells each. (B) PARP activation in infected HOS cells was measured at 12 and 24 h postinfection. Thirty micrograms of total protein was resolved on an 8% SDS-PAGE gel and probed with anti-PARP. (C) Cleavage of caspase 3 was examined in HOS cells infected with either vMyxlac or the M11L deletion mutant vMyxM11LKO at various times postinfection. Caspase 3 cleavage results in the production of three cleaved products. Normally only the 19- and 17-kDa fragments are picked up by the antibody. (D) Near-confluent monolayers of HOS or RK13 cells were infected with either vMyxlac or vMyxM11LKO. The monolayers were stained with 5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl-β-d-galactopyranoside (X-Gal) at 48 h postinfection and photographed under visible light with a Leica DMR-5 microscope. HOS and RK13 cells were infected at an MOI of 5, and infected cells were collected at the times indicated. Recovered virus was titrated on BGMK cells.
