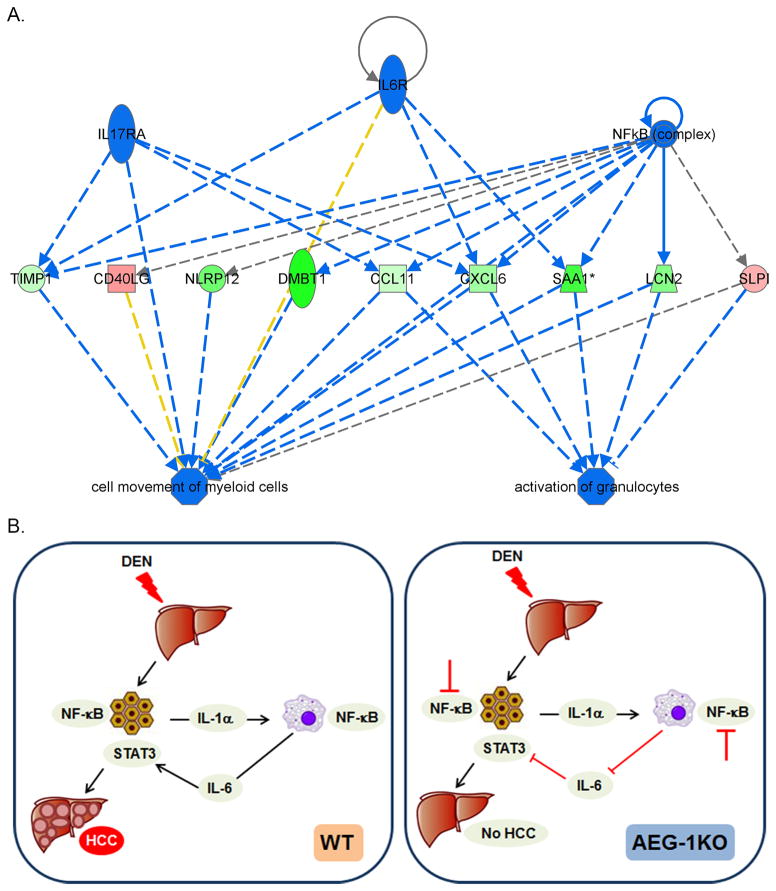
Fig. 6.
Molecular mechanism rendering AEG-1KO mice resistant to HCC. A. Functional endpoints, analyzed by Ingenuity pathway analysis, that are inhibited in AEG-1KO mice. Blue line: inhibition; red line: activation; yellow line: finding inconsistent with state of downstream molecules; gray line: effect not predicted. Green color: downregulation of expression; red color: upregulation of expression. B. Schematic representation of the molecular mechanism of resistance of AEG-1KO mice to HCC. In WT mice DEN-induced hepatocyte injury leads to IL-1α production that activates NF-κB in the macrophages leading to production of IL-6. IL-6 activates STAT3 in hepatocytes facilitating proliferation of the mutated cells leading to HCC. In AEG-1KO mice NF-κB activation is inhibited in hepatocytes and macrophages thereby inhibiting IL-6 production and STAT3 activation. As a consequence, HCC development is significantly abrogated.