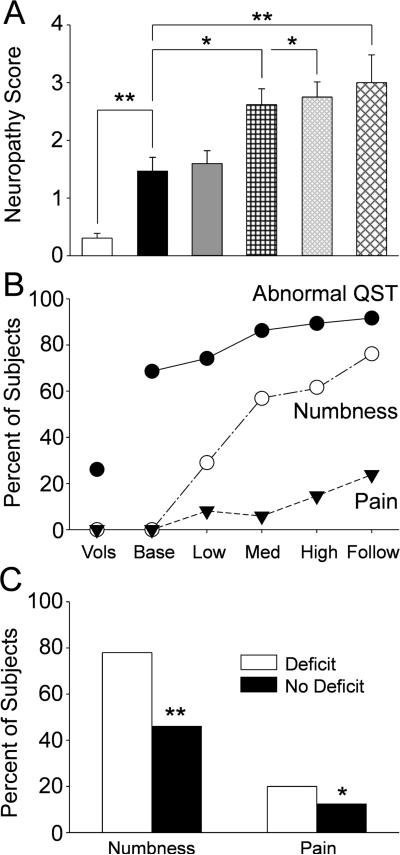
Figure 6.
The bar graphs in A show the mean and standard error for the neuropathy score (total number of QST measures 2 standard deviations or more from the healthy volunteer mean) for the for the healthy volunteers (“Vols” open bars) and the patients at the pretreatment baseline (“Base”, black bars) and at each cumulative dose treatment category (“Low” is up to 370.6 mg, gray bars; medium (Med) is up to 795.6 mg, black cross hatch; “High” is up to 2328.2 mg, gray diagonal narrow cross hatch; and “Follow” is 6 months after tretament, black diagonal wide cross hatch). The horizontal lines indicate the statistical comparions made. The scatter and line plot in B shows the percentage of healthy volunteers and patients at each treatment category (abbreviations as above) that had abnormal QST measures (out of range measures as defined above, black circles) or that reported numbness (open circles) or pain (filled triangles). Finally, the bar graphs in C shows the percentage of patients that reported numbness or pain at the end of treatment categorized on whether they had any QST deficit (open bars) or not (black bars) at the pretretament baseline assessment. * = p<0.05; ** = p<0.01; *** = p<0.001.