FIG. 2.
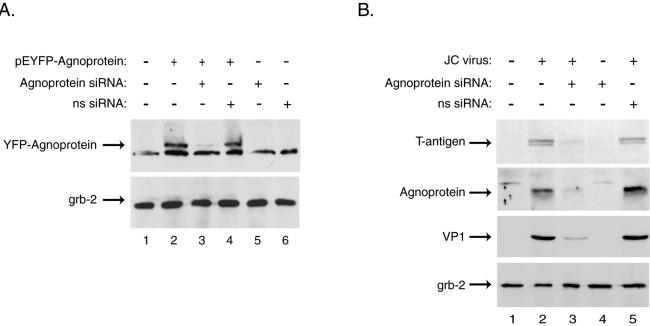
JCV agnoprotein siRNA decreases agnoprotein expression as well as that of other viral proteins in primary human astrocytes. Primary human fetal astrocyte preparations, transient transfections, siRNA treatments, and Western blotting were performed as described in the text and the legend to Fig. 1. The cells were transfected with a plasmid containing JCV agnoprotein fused to YFP (6). The JCV agnoprotein siRNA targeted nt 324 to 342 of the Mad-1 isolate of JCV (sense strand, 5′-AACCUGGAGUGGAACUAAAdTdT-3′), while a nonspecific siRNA (ns siRNA) targeted nt 435 to 453 of the Dunlop strain of BKV (sense strand, 5′-AACCUGGACUGGAACAAAAdTdT-3′). The two base pair mismatches between JCV and BKV agnoprotein sequences are underlined. (A) Whole-cell extracts prepared from transfected astrocytes 24 h after treatment with specific or nonspecific siRNA were analyzed by Western blotting for the presence of agnoprotein and the unrelated cellular factor Grb-2 (upper and lower panels, respectively). (B) Primary astrocytes that were uninfected or infected with the JCV Mad-4 strain were then transfected with JCV agnoprotein or nonspecific BKV agnoprotein siRNA at days 1, 5, and 10 postinfection and were harvested at day 15. Western blotting was performed on whole-cell extracts for presence of the JCV T antigen, agnoprotein, and VP1 as well as the cellular protein Grb-2.
